Gough Whitlam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Edward Gough Whitlam (11 July 191621 October 2014) was the 21st
prime minister of Australia
The prime minister of Australia is the head of government of the Commonwealth of Australia. The prime minister heads the executive branch of the Australian Government, federal government of Australia and is also accountable to Parliament of A ...
, serving from 1972 to 1975. The longest-serving federal leader of the Australian Labor Party
The Australian Labor Party (ALP), also simply known as Labor, is the major centre-left political party in Australia, one of two major parties in Australian politics, along with the centre-right Liberal Party of Australia. The party forms the f ...
(ALP) from 1967 to 1977, he was notable for being the head of a reformist
Reformism is a political doctrine advocating the reform of an existing system or institution instead of its abolition and replacement.
Within the socialist movement, reformism is the view that gradual changes through existing institutions can eve ...
and socially progressive administration that extraordinarily ended with his removal as prime minister after controversially being dismissed by the governor-general of Australia
The governor-general of Australia is the representative of the monarch, currently King Charles III, in Australia.John Kerr, at the climax of the
 Edward Gough Whitlam was born on 11 July 1916 at the family home 'Ngara', 46 Rowland Street,
Edward Gough Whitlam was born on 11 July 1916 at the family home 'Ngara', 46 Rowland Street, 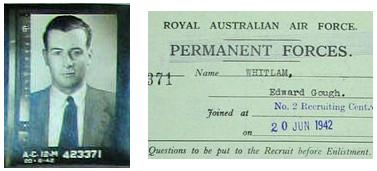 Whitlam enrolled at St Paul's College at the
Whitlam enrolled at St Paul's College at the
 Soon after the outbreak of World War II in 1939, Whitlam enlisted in the
Soon after the outbreak of World War II in 1939, Whitlam enlisted in the

 With his war service loan, Whitlam built a house in seaside
With his war service loan, Whitlam built a house in seaside  The ALP had been out of office since the Chifley Government's defeat in 1949 and, since 1951, had been under the leadership of
The ALP had been out of office since the Chifley Government's defeat in 1949 and, since 1951, had been under the leadership of
 Whitlam believed the Labor Party had little chance of being elected unless it could expand its appeal from the traditional working-class base to include the suburban middle class. He sought to shift control of the ALP from union officials to the parliamentary party, and hoped even rank-and-file party members could be given a voice in the conference. In 1968, controversy erupted within the party when the executive refused to seat new Tasmanian delegate
Whitlam believed the Labor Party had little chance of being elected unless it could expand its appeal from the traditional working-class base to include the suburban middle class. He sought to shift control of the ALP from union officials to the parliamentary party, and hoped even rank-and-file party members could be given a voice in the conference. In 1968, controversy erupted within the party when the executive refused to seat new Tasmanian delegate
 Soon after taking the leadership, Whitlam reorganised the ALP caucus, assigning portfolios and turning the Labor frontbench into a shadow cabinet. While the Liberal-Country Coalition had a huge majority in the House of Representatives, Whitlam energised the party by campaigning intensively to win two by-elections in 1967: first in Corio in Victoria, and later that year in Capricornia in Queensland. The November half-Senate election saw a moderate swing to Labor and against the Coalition, compared with the general election the previous year. These federal victories, in which both Whitlam and Holt campaigned, helped give Whitlam the leverage he needed to carry out party reforms.
At the end of 1967, Holt vanished while swimming in rough seas near Melbourne; his body was never recovered. John McEwen, as leader of the junior Coalition partner, the Country Party, took over as prime minister for three weeks until the Liberals could elect a new leader. Senator
Soon after taking the leadership, Whitlam reorganised the ALP caucus, assigning portfolios and turning the Labor frontbench into a shadow cabinet. While the Liberal-Country Coalition had a huge majority in the House of Representatives, Whitlam energised the party by campaigning intensively to win two by-elections in 1967: first in Corio in Victoria, and later that year in Capricornia in Queensland. The November half-Senate election saw a moderate swing to Labor and against the Coalition, compared with the general election the previous year. These federal victories, in which both Whitlam and Holt campaigned, helped give Whitlam the leverage he needed to carry out party reforms.
At the end of 1967, Holt vanished while swimming in rough seas near Melbourne; his body was never recovered. John McEwen, as leader of the junior Coalition partner, the Country Party, took over as prime minister for three weeks until the Liberals could elect a new leader. Senator  In March 1971, the resentment against Gorton came to a head when a confidence vote in the Liberal caucus resulted in a tie. Declaring that this was a sign he no longer had the confidence of the party, Gorton resigned, and William McMahon was elected his successor. With the Liberals in turmoil, Whitlam and the ALP sought to gain public trust as a credible government-in-waiting. The party's actions, such as its abandonment of the White Australia policy, gained favourable media attention. The Labor leader flew to
In March 1971, the resentment against Gorton came to a head when a confidence vote in the Liberal caucus resulted in a tie. Declaring that this was a sign he no longer had the confidence of the party, Gorton resigned, and William McMahon was elected his successor. With the Liberals in turmoil, Whitlam and the ALP sought to gain public trust as a credible government-in-waiting. The party's actions, such as its abandonment of the White Australia policy, gained favourable media attention. The Labor leader flew to  By early 1972, Labor had established a clear lead in the polls; indeed, for the first time since 1955 its support was greater than the combined vote for the Coalition and DLP. Unemployment was at a ten-year peak, rising to 2.14 per cent in August (though the unemployment rate was calculated differently compared to the present, and did not include thousands of rural workers on Commonwealth-financed relief work). Inflation was also at its highest rate since the early 1950s. The government recovered slightly in the August Budget session of Parliament, proposing income tax cuts and increased spending. The Labor strategy for the run-up to the election was to sit back and allow the Coalition to make mistakes. Whitlam controversially stated in March "draft-dodging is not a crime" and that he would be open to a revaluation of the Australian dollar. With the Coalition sinking in the polls and his own personal approval ratings down as low as 28 per cent, McMahon waited as long as he could, finally calling an election for the House of Representatives for 2December. Whitlam noted that the polling day was the anniversary of the
By early 1972, Labor had established a clear lead in the polls; indeed, for the first time since 1955 its support was greater than the combined vote for the Coalition and DLP. Unemployment was at a ten-year peak, rising to 2.14 per cent in August (though the unemployment rate was calculated differently compared to the present, and did not include thousands of rural workers on Commonwealth-financed relief work). Inflation was also at its highest rate since the early 1950s. The government recovered slightly in the August Budget session of Parliament, proposing income tax cuts and increased spending. The Labor strategy for the run-up to the election was to sit back and allow the Coalition to make mistakes. Whitlam controversially stated in March "draft-dodging is not a crime" and that he would be open to a revaluation of the Australian dollar. With the Coalition sinking in the polls and his own personal approval ratings down as low as 28 per cent, McMahon waited as long as he could, finally calling an election for the House of Representatives for 2December. Whitlam noted that the polling day was the anniversary of the
 Whitlam took office with a majority in the House of Representatives, but without control of the Senate (elected in the 1967 and 1970 half-elections). The Senate at that time consisted of ten members from each of the six states, elected by
Whitlam took office with a majority in the House of Representatives, but without control of the Senate (elected in the 1967 and 1970 half-elections). The Senate at that time consisted of ten members from each of the six states, elected by
 The McMahon government had consisted of 27 ministers, twelve of whom comprised the Cabinet. In the run-up to the election, the Labor caucus had decided that if the party took power all 27 ministers were to be Cabinet members. Intense canvassing took place amongst ALP parliamentarians as the duumvirate did its work, and on 18 December the caucus elected the Cabinet. The results were generally acceptable to Whitlam, and within three hours, he had announced the portfolios of the Cabinet members. To give himself greater control over the Cabinet, in January 1973 Whitlam established five Cabinet committees (with the members appointed by himself, not the caucus) and took full control of the Cabinet agenda.
Whitlam, prime minister for fewer than three years between 1972 and 1975, pushed through a raft of reforms that radically changed Australia's economic, legal and cultural landscape.
The Whitlam government abolished the death penalty for federal crimes.
The McMahon government had consisted of 27 ministers, twelve of whom comprised the Cabinet. In the run-up to the election, the Labor caucus had decided that if the party took power all 27 ministers were to be Cabinet members. Intense canvassing took place amongst ALP parliamentarians as the duumvirate did its work, and on 18 December the caucus elected the Cabinet. The results were generally acceptable to Whitlam, and within three hours, he had announced the portfolios of the Cabinet members. To give himself greater control over the Cabinet, in January 1973 Whitlam established five Cabinet committees (with the members appointed by himself, not the caucus) and took full control of the Cabinet agenda.
Whitlam, prime minister for fewer than three years between 1972 and 1975, pushed through a raft of reforms that radically changed Australia's economic, legal and cultural landscape.
The Whitlam government abolished the death penalty for federal crimes. 
 In February 1973, the Attorney General, Senator
In February 1973, the Attorney General, Senator
 Following the 1974
Following the 1974
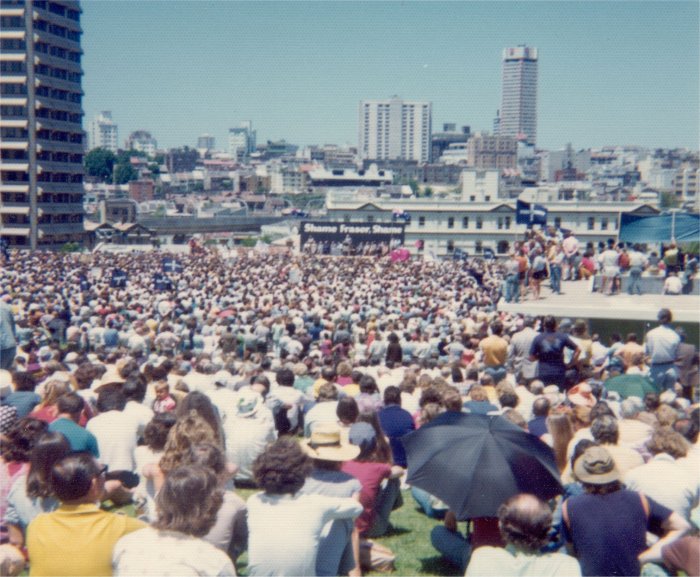 As the ALP began the 1975 campaign, it seemed that its supporters would maintain their rage. Early rallies drew huge crowds, with attendees handing Whitlam money to pay election expenses. The crowds greatly exceeded those in any of Whitlam's earlier campaigns; in The Domain, Sydney, 30,000 people gathered for an ALP rally below a banner: "Shame Fraser Shame". Fraser's appearances drew protests, and a letter bomb sent to Kerr was defused by authorities. Instead of making a policy speech to keynote his campaign, Whitlam made a speech attacking his opponents and calling 11 November "a day which will live in infamy".
Polls from the first week of campaigning showed a nine-point swing against Labor, which would have decimated Labor if repeated in an election. Whitlam's campaign team disbelieved the results at first, but additional polling returns clearly showed that the electorate had turned against Labor. The Coalition attacked Labor for economic conditions, and released television commercials with the title "The Three Dark Years" showing images from Whitlam government scandals. The ALP campaign concentrated on the issue of Whitlam's dismissal and did not address the economy until its final days. By that time Fraser was confident of victory and content to sit back, avoid specifics and make no mistakes. In the election, the Coalition won the largest majority government in Australian history, winning 91 seats to Labor's 36. Labor suffered a 6.5 per cent swing against it and its caucus was cut almost in half, suffering a 30-seat swing. Labor was left with five fewer seats than it had when Whitlam took the leadership. The Coalition also won a 37–25 majority in the Senate.
Whitlam stayed on as Opposition leader, surviving a leadership challenge. In early 1976, an additional controversy broke when it was reported that Whitlam had been involved in ALP attempts to raise $500,000 during the election from the
As the ALP began the 1975 campaign, it seemed that its supporters would maintain their rage. Early rallies drew huge crowds, with attendees handing Whitlam money to pay election expenses. The crowds greatly exceeded those in any of Whitlam's earlier campaigns; in The Domain, Sydney, 30,000 people gathered for an ALP rally below a banner: "Shame Fraser Shame". Fraser's appearances drew protests, and a letter bomb sent to Kerr was defused by authorities. Instead of making a policy speech to keynote his campaign, Whitlam made a speech attacking his opponents and calling 11 November "a day which will live in infamy".
Polls from the first week of campaigning showed a nine-point swing against Labor, which would have decimated Labor if repeated in an election. Whitlam's campaign team disbelieved the results at first, but additional polling returns clearly showed that the electorate had turned against Labor. The Coalition attacked Labor for economic conditions, and released television commercials with the title "The Three Dark Years" showing images from Whitlam government scandals. The ALP campaign concentrated on the issue of Whitlam's dismissal and did not address the economy until its final days. By that time Fraser was confident of victory and content to sit back, avoid specifics and make no mistakes. In the election, the Coalition won the largest majority government in Australian history, winning 91 seats to Labor's 36. Labor suffered a 6.5 per cent swing against it and its caucus was cut almost in half, suffering a 30-seat swing. Labor was left with five fewer seats than it had when Whitlam took the leadership. The Coalition also won a 37–25 majority in the Senate.
Whitlam stayed on as Opposition leader, surviving a leadership challenge. In early 1976, an additional controversy broke when it was reported that Whitlam had been involved in ALP attempts to raise $500,000 during the election from the
 Whitlam initially had a close relationship with Labor leader
Whitlam initially had a close relationship with Labor leader
 A state memorial service was held on 5November 2014 in the
A state memorial service was held on 5November 2014 in the
1975 Australian constitutional crisis
The 1975 Australian constitutional crisis, also known simply as the Dismissal, culminated on 11 November 1975 with the dismissal from office of the prime minister, Gough Whitlam of the Australian Labor Party (ALP), by Governor-General Sir Jo ...
. Whitlam is the only Australian prime minister to have been removed from office.
Whitlam served as an air navigator in the Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
for four years during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, and worked as a barrister
A barrister is a type of lawyer in common law jurisdictions. Barristers mostly specialise in courtroom advocacy and litigation. Their tasks include taking cases in superior courts and tribunals, drafting legal pleadings, researching law and ...
following the war. He was first elected to the Australian House of Representatives
The House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Australia, the upper house being the Senate. Its composition and powers are established in Chapter I of the Constitution of Australia.
The term of members of the ...
in 1952, becoming a member of parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
(MP) for the division of Werriwa
The Division of Werriwa is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales. The name Werriwa derives from a local Aboriginal name for Lake George, which was located in the division when it was established in 1900. The division ...
. Whitlam became deputy leader of the Labor Party in 1960, and in 1967, after the retirement of Arthur Calwell
Arthur Augustus Calwell (28 August 1896 – 8 July 1973) was an Australian politician who served as the leader of the Labor Party from 1960 to 1967. He led the party to three federal elections.
Calwell grew up in Melbourne and attended St J ...
, was elected leader of the party and became the Leader of the Opposition
The Leader of the Opposition is a title traditionally held by the leader of the largest political party not in government, typical in countries utilizing the parliamentary system form of government. The leader of the opposition is typically se ...
. After narrowly losing the 1969 federal election to John Gorton
Sir John Grey Gorton (9 September 1911 – 19 May 2002) was an Australian politician who served as the nineteenth Prime Minister of Australia, in office from 1968 to 1971. He led the Liberal Party during that time, having previously been a l ...
, Whitlam led Labor to victory at the 1972 election, after 23 years of continuous Coalition government
A coalition government is a form of government in which political parties cooperate to form a government. The usual reason for such an arrangement is that no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an election, an atypical outcome in ...
.
The Whitlam Government implemented a large number of new programmes and policy changes, including the termination of military conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day und ...
, institution of universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized ar ...
and free university education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completi ...
, and the implementation of legal aid
Legal aid is the provision of assistance to people who are unable to afford legal representation and access to the court system. Legal aid is regarded as central in providing access to justice by ensuring equality before the law, the right to co ...
programmes. With the opposition-controlled Australian Senate
The Senate is the upper house of the Bicameralism, bicameral Parliament of Australia, the lower house being the House of Representatives (Australia), House of Representatives. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Chapter ...
delaying passage of bills, Whitlam called a double dissolution
A double dissolution is a procedure permitted under the Australian Constitution to resolve deadlocks in the bicameral Parliament of Australia between the House of Representatives (lower house) and the Senate (upper house). A double dissolution ...
election in 1974 in which he won a slightly reduced majority in the House of Representatives, and picked up three Senate seats, although that was not enough to provide a majority in the Senate. The Whitlam government then instituted the first and only joint sitting
A joint session or joint convention is, most broadly, when two normally separate decision-making groups meet, often in a special session or other extraordinary meeting, for a specific purpose.
Most often it refers to when both houses of a bicamer ...
enabled under section 57 of the Australian constitution
The Constitution of Australia (or Australian Constitution) is a constitutional document that is supreme law in Australia. It establishes Australia as a federation under a constitutional monarchy and outlines the structure and powers of the ...
as part of the double dissolution process. Despite the government's second election victory, the opposition, reacting to government scandals and a declining economy suffering from the 1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
and the 1973–75 global recession, continued to obstruct the government's programme in the Senate.
In late 1975, the opposition senators refused to allow a vote on the government's appropriation bill
An appropriation, also known as supply bill or spending bill, is a proposed law that authorizes the expenditure of government funds. It is a bill that sets money aside for specific spending. In some democracies, approval of the legislature is ne ...
s, returning them to the House of Representatives with a demand that the government go to an election, thus denying the government supply
Supply may refer to:
*The amount of a resource that is available
**Supply (economics), the amount of a product which is available to customers
**Materiel, the goods and equipment for a military unit to fulfill its mission
*Supply, as in confidenc ...
. Whitlam refused to agree to the request, arguing that his government, which held a clear majority in the House of Representatives, was being held to ransom by the Senate. The crisis ended in mid-November, when governor-general Sir John Kerr dismissed him from office and commissioned the opposition leader, Malcolm Fraser
John Malcolm Fraser (; 21 May 1930 – 20 March 2015) was an Australian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Australia from 1975 to 1983, holding office as the leader of the Liberal Party of Australia.
Fraser was raised on hi ...
, as caretaker prime minister. Labor lost the subsequent election by a landslide. Whitlam stepped down as leader of the party after losing again at the 1977 election, and retired from parliament the following year. Upon the election of the Hawke Government in 1983, he was appointed as Ambassador to UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
, a position he filled with distinction, and was elected a member of the UNESCO Executive Board. He remained active into his nineties. The propriety and circumstances of his dismissal and the legacy of his government have been frequently debated in the decades since he left office. Nevertheless, journalist Paul Kelly said that "there is no doubt that in three years his government was responsible for more reforms and innovations than any other government in Australian history".
Early life
 Edward Gough Whitlam was born on 11 July 1916 at the family home 'Ngara', 46 Rowland Street,
Edward Gough Whitlam was born on 11 July 1916 at the family home 'Ngara', 46 Rowland Street, Kew
Kew () is a district in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames. Its population at the 2011 census was 11,436. Kew is the location of the Royal Botanic Gardens ("Kew Gardens"), now a World Heritage Site, which includes Kew Palace. Kew is a ...
, a suburb of Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
, the elder of two children (his sister, Freda Freda may refer to:
* Frida (given name), also spelled ''Freda''
* Freda (surname)
* Freda (character) from The Lord of the Rings film trilogy
* Ford Freda, a motor vehicle introduced in the Japanese market in 1995
* Freda Sandstone, a member of t ...
, was born four years after him), to Martha (née Maddocks) and Fred Whitlam. His father was a federal public servant who later served as Commonwealth Crown Solicitor, and Whitlam senior's involvement in human rights issues was a powerful influence on his son. Since his maternal grandfather was also named Edward, from early childhood he was called by his middle name, Gough, which in turn had come from his paternal grandfather who had been named after the British soldier Field-Marshal Hugh Gough, 1st Viscount Gough
Field Marshal Hugh Gough, 1st Viscount Gough, (3 November 1779 – 2 March 1869) was an Irish officer of the British Army. After serving as a junior officer at the seizure of the Cape of Good Hope during the French Revolutionary Wars, Gough com ...
.
In 1918, Fred Whitlam was promoted to deputy Crown solicitor and transferred to Sydney. The family lived first in the North Shore suburb of Mosman
Mosman is a suburb on the Lower North Shore region of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Mosman is located 8 kilometres north-east of the Sydney central business district and is the administrative centre for the local governm ...
and then in Turramurra
Turramurra is a suburb on the Upper North Shore of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is located north-west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of Ku-ring-gai Council. It shares the postc ...
. At age six, Gough began his education at Chatswood Church of England Girls' School (early primary schooling at a girls' school was not unusual for small boys at the time). After a year there, he attended Mowbray House School
Mowbray House is a heritage-listed historic building that was an independent, day and boarding school for boys, located in Chatswood, on the North Shore of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. More recently, it was part of an Ausgrid depot ...
and Knox Grammar School
, motto_translation = The Manly Thing Is Being Done
, established =
, founder = John Gilmore, William McIlrath, Robert Gillespie and Andrew Reid
, type = Independent, day & boarding ...
in the suburbs of Sydney.
Fred Whitlam was promoted again in 1927, this time to Assistant Crown Solicitor. The position was located in the new national capital of Canberra
Canberra ( )
is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The ci ...
, and the Whitlam family moved there. As of 2008, Whitlam was the only prime minister to have spent his formative years in Canberra. At the time, conditions remained primitive in what was dubbed "the bush capital" and "the land of the blowflies". Gough attended the government Telopea Park School
, image = Telopea Park School in Barton (1).jpg
, image_size = 250
, caption =
, motto = la, Spectans orientia solis lumina
, motto_translation = Looking towards the rising sun
, established =
, type = Government ...
. In 1932, Whitlam's father transferred him to Canberra Grammar School where, at the Speech Day ceremony that year, he was awarded a prize by the Governor-General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
, Sir Isaac Isaacs
Sir Isaac Alfred Isaacs (6 August 1855 – 11 February 1948) was an Australian lawyer, politician, and judge who served as the ninth Governor-General of Australia, in office from 1931 to 1936. He had previously served on the High Court of A ...
.
 Whitlam enrolled at St Paul's College at the
Whitlam enrolled at St Paul's College at the University of Sydney
The University of Sydney (USYD), also known as Sydney University, or informally Sydney Uni, is a public research university located in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in Australia and is one of the country's si ...
at the age of 18. He earned his first wages by appearing, with several other "Paulines", in a cabaret scene in the film '' The Broken Melody''the students were chosen because St Paul's required formal wear at dinner, and they could therefore supply their own costumes. After receiving a Bachelor of Arts degree with second-class honours in classics, Whitlam remained at St Paul's to begin his law studies. He had originally contemplated an academic career, but his lacklustre marks made that unlikely. Dropping out of Greek classes, he professed himself unable to care for the "dry as dust" lectures of Enoch Powell
John Enoch Powell, (16 June 1912 – 8 February 1998) was a British politician, classical scholar, author, linguist, soldier, philologist, and poet. He served as a Conservative Member of Parliament (1950–1974) and was Minister of Health (1 ...
.
Military service
 Soon after the outbreak of World War II in 1939, Whitlam enlisted in the
Soon after the outbreak of World War II in 1939, Whitlam enlisted in the Sydney University Regiment
Sydney University Regiment (SUR) is an officer-training regiment of the Australian Army Reserve. Its predecessor, the University Volunteer Rifle Corps, was raised in 1900 as a unit of the colonial New South Wales Defence Force. During the 20th ...
, part of the Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
. In late 1941, following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
, and with a year remaining in his legal studies, he volunteered for the Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
(RAAF). In 1942, while awaiting entry into the service, Whitlam met and married Margaret Elaine Dovey, who had swum for Australia in the 1938 British Empire Games and was the daughter of barrister and future New South Wales Supreme Court judge Bill Dovey
Wilfred Robert Dovey Queen's Counsel, QC (10 April 189412 December 1969) was an Australian barrister and judge. He served on the Supreme Court of New South Wales from 1953 to 1964. He was described as colourful, slightly eccentric and irascible, ...
. He entered the RAAF on 20 June 1942.
Whitlam trained as a navigator and bomb aimer, before serving with No. 13 Squadron RAAF
No. 13 (City of Darwin) Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) squadron. The unit saw combat during World War II as a bomber and maritime patrol squadron and is currently active as a mixed regular and reserve RAAF unit located in Darwi ...
, based mainly on the Gove Peninsula
The Gove Peninsula is at the northeastern corner of Arnhem Land in the Northern Territory of Australia. The peninsula became strategically important during World War II when a Royal Australian Air Force base was constructed at what is now Gove ...
, Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an states and territories of Australia, Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory ...
, flying Lockheed Ventura
The Lockheed Ventura is a twin-engine medium bomber and patrol bomber of World War II.
The Ventura first entered combat in Europe as a bomber with the RAF in late 1942. Designated PV-1 by the United States Navy (US Navy), it entered combat in 1 ...
bombers. He reached the rank of Flight Lieutenant
Flight lieutenant is a junior commissioned rank in air forces that use the Royal Air Force (RAF) system of ranks, especially in Commonwealth countries. It has a NATO rank code of OF-2. Flight lieutenant is abbreviated as Flt Lt in the India ...
. While in the service, he began his political activities, distributing literature for the Australian Labor Party
The Australian Labor Party (ALP), also simply known as Labor, is the major centre-left political party in Australia, one of two major parties in Australian politics, along with the centre-right Liberal Party of Australia. The party forms the f ...
during the 1943 federal election and urging the passage of the "Fourteen Powers" referendum of 1944, which would have expanded the powers of the federal government. Although the party was victorious, the referendum it advocated was defeated. In 1961, Whitlam said of the referendum defeat, "My hopes were dashed by the outcome and from that moment I determined to do all I could do to modernise the Australian Constitution." While still in uniform, Whitlam joined the ALP in Sydney in 1945. He was discharged from the RAAF on 17 October 1945, and continued to use Air Force log books to record all the flights he took until 2007. Whitlam completed his studies after the war, obtained his Bachelor of Laws, and was admitted to the federal and New South Wales bars in 1947.
Early political career, 1952–1967
Member of Parliament, 1952–1960

 With his war service loan, Whitlam built a house in seaside
With his war service loan, Whitlam built a house in seaside Cronulla
Cronulla is a suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Boasting numerous surf beaches and swimming spots, the suburb attracts both tourists and Greater Sydney residents. Cronulla is located 26 kilometres south of the Sydne ...
. He also bought the block of land next door, using the prize money (£1,000 in security bonds) he received for winning the Australian National Quiz Championship in 1948 and 1949 (he was runner-up in 1950). He sought to make a career in the ALP there, but local Labor supporters were sceptical of Whitlam's loyalties, given his privileged background. In the postwar years, he practised law, concentrating on landlord/tenant matters, and sought to build his bona fides in the party. He ran twiceunsuccessfullyfor the local council, once (also unsuccessfully) for the New South Wales Legislative Assembly
The New South Wales Legislative Assembly is the lower of the two houses of the Parliament of New South Wales, an Australian state. The upper house is the New South Wales Legislative Council. Both the Assembly and Council sit at Parliament Ho ...
, and campaigned for other candidates. In 1951, Bert Lazzarini
Hubert Peter Lazzarini (8 September 1884 – 1 October 1952) was an Australian politician. He was a member of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) and represented the Division of Werriwa in the House of Representatives for over 30 years (1919–1931 ...
, the Labor member for the Federal electorate of Werriwa
The Division of Werriwa is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales. The name Werriwa derives from a local Aboriginal name for Lake George, which was located in the division when it was established in 1900. The division ...
, announced that he would stand down at the next election. Whitlam won the preselection
Preselection is the process by which a candidate is selected, usually by a political party, to contest an election for political office. It is also referred to as candidate selection. It is a fundamental function of political parties. The presele ...
as ALP candidate. Lazzarini died in 1952 before completing his term and Whitlam was elected to the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
in the ensuing by-election on 29 November 1952. Whitlam trebled Lazzarini's majority in a 12 per cent swing to Labor.
Whitlam joined the ALP minority in the House of Representatives. His maiden speech
A maiden speech is the first speech given by a newly elected or appointed member of a legislature or parliament.
Traditions surrounding maiden speeches vary from country to country. In many Westminster system governments, there is a convention th ...
provoked an interruption by a future prime minister, John McEwen
Sir John McEwen, (29 March 1900 – 20 November 1980) was an Australian politician who served as the 18th prime minister of Australia, holding office from 1967 to 1968 in a caretaker capacity after the disappearance of Harold Holt. He was the ...
, who was then told by the Speaker
Speaker may refer to:
Society and politics
* Speaker (politics), the presiding officer in a legislative assembly
* Public speaker, one who gives a speech or lecture
* A person producing speech: the producer of a given utterance, especially:
** I ...
that maiden speeches are traditionally heard in silence. Whitlam responded to McEwen by saying Benjamin Disraeli
Benjamin Disraeli, 1st Earl of Beaconsfield, (21 December 1804 – 19 April 1881) was a British statesman and Conservative politician who twice served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. He played a central role in the creation o ...
had been heckled in his maiden speech and had responded, "The time will come when you shall hear me." He told McEwen, "The time will come when you may interrupt me." According to early Whitlam biographers Laurie Oakes
Laurie Oakes (born 14 August 1943 in Newcastle, New South Wales) is an Australian retired journalist. He worked in the Canberra Press Gallery from 1969 to 2017, covering the Parliament of Australia and federal elections for print, radio, and t ...
and David Solomon, this cool response put the Coalition government on notice that the new Member for Werriwa would be a force to be reckoned with.
In the rough and tumble debate in the House of Representatives, Whitlam called fellow MHR Bill Bourke
William Meskill Bourke (2 June 1913 – 22 May 1981) was an Australian politician.
Bourke was elected to the Australian House of Representatives seat of Fawkner at the 1949 election representing the Australian Labor Party. He was expelled f ...
"this grizzling Quisling
''Quisling'' (, ) is a term used in Scandinavian languages and in English meaning a citizen or politician of an occupied country who collaborates with an enemy occupying force – or more generally as a synonym for ''traitor''. The word ori ...
", Garfield Barwick
Sir Garfield Edward John Barwick, (22 June 190313 July 1997) was an Australian judge who was the seventh and longest serving Chief Justice of Australia, in office from 1964 to 1981. He had earlier been a Liberal Party politician, serving as a ...
(who, as High Court Chief Justice, played a role in Whitlam's downfall) a "bumptious bastard", and he said Bill Wentworth
William Charles Wentworth (8 September 1907 – 15 June 2003), usually known as Bill Wentworth and sometimes referred to by others as William Charles Wentworth IV, was an Australian politician. He was a member of the Liberal Party for most of ...
exhibited a "hereditary streak of insanity". After calling future prime minister William McMahon
Sir William McMahon (23 February 190831 March 1988) was an Australian politician who served as the 20th Prime Minister of Australia, in office from 1971 to 1972 as leader of the Liberal Party. He was a government minister for over 21 years, t ...
a " quean", he apologised.
 The ALP had been out of office since the Chifley Government's defeat in 1949 and, since 1951, had been under the leadership of
The ALP had been out of office since the Chifley Government's defeat in 1949 and, since 1951, had been under the leadership of Bert Evatt
Herbert Vere Evatt, (30 April 1894 – 2 November 1965) was an Australian politician and judge. He served as a judge of the High Court of Australia from 1930 to 1940, Attorney-General and Minister for External Affairs from 1941 to 1949, and ...
, whom Whitlam greatly admired. In 1954, the ALP seemed likely to return to power. The Prime Minister, Robert Menzies
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory ...
, adroitly used the defection of a Soviet official to his advantage, and his coalition of the Liberal and Country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the ...
parties was returned in the 1954 election with a seven-seat majority. After the election, Evatt attempted to purge the party of industrial groupers, who had long dissented from party policy, and who were predominantly Catholic and anti-communist. The ensuing division in the ALP, which came to be known as " The Split", sparked the birth of the Democratic Labor Party (DLP). It was a conflict that helped to keep Labor out of power for a generation, since DLP supporters chose the Liberal Party in preferential voting {{short description, Election systems
Preferential voting or preference voting (PV) may refer to different election systems or groups of election systems:
* Ranked voting methods, all election methods that involve ranking candidates in order of pr ...
. Whitlam supported Evatt throughout this period.
In 1955, a redistribution divided Whitlam's electorate of Werriwa in two, with his Cronulla home located in the new electorate of Hughes
Hughes may refer to:
People
* Hughes (surname)
* Hughes (given name)
Places Antarctica
* Hughes Range (Antarctica), Ross Dependency
* Mount Hughes, Oates Land
* Hughes Basin, Oates Land
* Hughes Bay, Graham Land
* Hughes Bluff, Victoria La ...
. Although Whitlam would have received ALP support in either division, he chose to continue standing for Werriwa and moved from Cronulla to Cabramatta
Cabramatta ('Cabra') is a suburb in south-western Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Cabramatta is located south-west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Fairfield.
Cabramat ...
. This meant even longer journeys for his older children to attend school, since neither electorate had a high school at the time, and they attended school in Sydney.
Whitlam was appointed to the Parliamentary Joint Committee on Constitutional Review in 1956. Biographer Jenny Hocking calls his service on the committee, which included members from all parties in both chambers of Parliament, one of the "great influences in his political development". According to Hocking, service on the committee caused Whitlam to focus not on internal conflicts consuming the ALP, but on Labor goals which were possible and worthwhile in the constitutional framework. Many Labor goals, such as nationalisation, ran contrary to the Constitution. Whitlam came to believe the Constitutionand especially Section 96 (which allowed the federal government to make grants to the states)could be used to advance a worthwhile Labor programme.
Deputy Leader, 1960–1967
By the late 1950s Whitlam was seen as a leadership contender once the existing Labor leaders exited the scene. Most of the party's major figures, including Evatt, Deputy LeaderArthur Calwell
Arthur Augustus Calwell (28 August 1896 – 8 July 1973) was an Australian politician who served as the leader of the Labor Party from 1960 to 1967. He led the party to three federal elections.
Calwell grew up in Melbourne and attended St J ...
, Eddie Ward
Edward John Ward (7 March 189931 July 1963) was an Australian politician who represented the Australian Labor Party (ALP) in federal parliament for over 30 years. He was the member for East Sydney for all but six-and-a-half weeks from 1931 u ...
, and Reg Pollard Reg Pollard may refer to:
* Reg Pollard (politician)
Reginald Thomas Pollard (31 October 1894 – 24 August 1981) was an Australian politician. He was a member of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) and served in the Victorian Legislative Assembl ...
, were in their sixties, twenty years older than Whitlam. In 1960, after losing three elections, Evatt resigned and was replaced by Calwell, with Whitlam defeating Ward for deputy leader. Calwell came within a handful of votes of winning the cliffhanger 1961 election. He had not wanted Whitlam as deputy leader, and believed Labor would have won if Ward had been in the position.
Soon after the 1961 election, events began to turn against Labor. When President Sukarno
Sukarno). (; born Koesno Sosrodihardjo, ; 6 June 1901 – 21 June 1970) was an Indonesian statesman, orator, revolutionary, and nationalist who was the first president of Indonesia, serving from 1945 to 1967.
Sukarno was the leader of ...
of Indonesia announced that he intended to take over West New Guinea
Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region ...
as the colonial Dutch departed, Calwell responded by declaring that Indonesia must be stopped by force. Calwell's statement was called "crazy and irresponsible" by Prime Minister Menzies, and the incident reduced public support for the ALP. At that time, the Federal Conference of the Labor Party, which dictated policy to parliamentary members, consisted of six members from each state, but not Calwell or Whitlam. In early 1963 a special conference met in a Canberra hotel to determine Labor policy regarding a proposed US base in northern Australia; Calwell and Whitlam were photographed by ''The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was fo ...
'' peering in through the doors, waiting for the verdict. In an accompanying story, Alan Reid of the ''Telegraph'' wrote that Labor was ruled by "36 faceless men
Faceless men is a term from Politics of Australia, Australian politics. The term is generally used to refer to men and women who exert Politics, political influence and are not elected representatives to state, territory or federal legislative bodi ...
". The Liberals seized on it, issuing a leaflet called "Mr Calwell and the Faceless Men" which accused Calwell and Whitlam of taking direction from "36 unknown men, not elected to Parliament nor responsible to the people".
Menzies manipulated the Opposition on issues that bitterly divided it, such as direct aid to the states for private schools, and the proposed base. He called an early election for November 1963, standing in support of those two issues. The Prime Minister performed better than Calwell on television and received an unexpected boost after the assassination of US President John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
. As a result, the Coalition easily defeated Labor on a 10-seat swing. Whitlam had hoped Calwell would step down after 1963, but he remained, reasoning that Evatt had been given three opportunities to win, and that he should be allowed a third try. Calwell dismissed proposals that the ALP leader and deputy leader should be entitled to membership of the party's conference (or on its governing 12-person Federal Executive, which had two representatives from each state), and instead ran successfully for one of the conference's Victoria seats. Labor did badly in a 1964 by-election in the Tasmanian electorate of Denison, and lost seats in the 1964 half-Senate election. The party was also defeated in the state elections in the most populous state, New South Wales, surrendering control of the state government for the first time since 1941.
Whitlam's relationship with Calwell, never good, deteriorated further after publication of a 1965 article in ''The Australian
''The Australian'', with its Saturday edition, ''The Weekend Australian'', is a broadsheet newspaper published by News Corp Australia since 14 July 1964.Bruns, Axel. "3.1. The active audience: Transforming journalism from gatekeeping to gatew ...
''. The article reported off-the-record comments Whitlam had made that his leader was "too old and weak" to win office, and that the party might be gravely damaged by an "old-fashioned" 70-year-old Calwell seeking his first term as prime minister. Later that year, at Whitlam's and Don Dunstan
Donald Allan Dunstan (21 September 1926 – 6 February 1999) was an Australian politician who served as the 35th premier of South Australia from 1967 to 1968, and again from 1970 to 1979. He was a member of the House of Assembly (MHA) for th ...
's urging, and over Calwell's objection, the biennial party conference made major changes to the party's platform: deleting support for the White Australia policy
The White Australia policy is a term encapsulating a set of historical policies that aimed to forbid people of non-European ethnic origin, especially Asians (primarily Chinese) and Pacific Islanders, from immigrating to Australia, starting i ...
and making the ALP's leader and deputy leader ''ex officio'' members of the conference and executive, along with the party's leader and deputy leader in the Senate. As Whitlam considered the Senate unrepresentative, he opposed the admission of its ALP leaders to the party's governing bodies.
Menzies retired in January 1966, and was succeeded as prime minister by the new Liberal Party leader, Harold Holt
Harold Edward Holt (5 August 190817 December 1967) was an Australian politician who served as the 17th prime minister of Australia from 1966 until his presumed death in 1967. He held office as leader of the Liberal Party.
Holt was born in S ...
. After years of politics being dominated by the elderly Menzies and Calwell, the younger Holt was seen as a breath of fresh air, and attracted public interest and support in the run-up to the November election.
In early 1966, the 36-member conference, with Calwell's assent, banned any ALP parliamentarian from supporting federal assistance to the states for spending on both government and private schools, commonly called "state aid". Whitlam broke with the party on the issue, and was charged with gross disloyalty by the executive, an offence which carried the penalty of expulsion from the party. Before the matter could be heard, Whitlam left for Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
, where he campaigned intensively for the ALP candidate Rex Patterson
Rex Alan Patterson (8 January 1927 – 13 April 2016) was an Australian politician. He was a member of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) and held ministerial office in the Whitlam Government as Minister for Northern Development (1972–1975), ...
in the Dawson by-election. The ALP won, dealing the government its first by-election defeat since 1952. Whitlam survived the expulsion vote by a margin of only two, gaining both Queensland votes. At the end of April, Whitlam challenged Calwell for the leadership; though Calwell received two-thirds of the vote, he announced that if the party lost the upcoming election, he would not stand again for the leadership.
Holt called an election for November 1966, in which Australia's involvement in the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
was a major issue. Calwell called for an "immediate and unconditional withdrawal" of Australian troops from Vietnam. Whitlam, however, said this would deprive Australia of any voice in a settlement, and that regular troops, rather than conscripts, should remain under some circumstances. Calwell considered Whitlam's remark disastrous, disputing the party line just five days before the election. The ALP suffered a crushing defeat; the party was reduced to 41 seats in the House of Representatives. Shortly after the election, Whitlam faced another expulsion vote for his stance on Vietnam, and survived. True to his word, Calwell resigned two months after the election. At the caucus
A caucus is a meeting of supporters or members of a specific political party or movement. The exact definition varies between different countries and political cultures.
The term originated in the United States, where it can refer to a meeting ...
meeting on 8February 1967, Whitlam was elected party leader, defeating leading left-wing candidate Dr Jim Cairns
James Ford Cairns (4 October 191412 October 2003) was an Australian politician who was prominent in the Labor movement through the 1960s and 1970s, and was briefly Treasurer and Deputy Prime Minister in the Whitlam government. He is best re ...
.
Leader of the Opposition, 1967–1972
Reforming the ALP
 Whitlam believed the Labor Party had little chance of being elected unless it could expand its appeal from the traditional working-class base to include the suburban middle class. He sought to shift control of the ALP from union officials to the parliamentary party, and hoped even rank-and-file party members could be given a voice in the conference. In 1968, controversy erupted within the party when the executive refused to seat new Tasmanian delegate
Whitlam believed the Labor Party had little chance of being elected unless it could expand its appeal from the traditional working-class base to include the suburban middle class. He sought to shift control of the ALP from union officials to the parliamentary party, and hoped even rank-and-file party members could be given a voice in the conference. In 1968, controversy erupted within the party when the executive refused to seat new Tasmanian delegate Brian Harradine
Richard William Brian Harradine (9 January 1935 – 14 April 2014) was an Australian politician who served as an independent member of the Australian Senate, from 1975 to 2005, representing the state of Tasmania. He was the longest-serving indep ...
, a Whitlam supporter who was considered a right-wing extremist. Whitlam resigned the leadership, demanding a vote of confidence from caucus. He defeated Cairns for the leadership in an unexpectedly close 38–32 vote. Despite the vote, the executive refused to seat Harradine.
With the ALP's governing bodies unwilling to reform themselves, Whitlam worked to build support for change among ordinary party members. He was successful in reducing union influence in the party, though he was never able to give the rank and file a direct vote in selecting the executive. The Victoria branch of the party had long been a problem; its executive was far to the left of the rest of the ALP, and had little electoral success. Whitlam was able to reconstruct the Victoria party organisation against the will of its leaders, and the reconstituted state party proved essential to victory in the 1972 election.
By the time of the 1969 party conference, Whitlam had gained considerable control over the ALP. That conference passed 61 resolutions, including broad changes to party policy and procedures. It called for the establishment of an Australian Schools Commission to consider the proper level of state aid for schools and universities, recognition of Aboriginal land claims, and expanded party policy on universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized ar ...
. The conference also called for increased federal involvement in urban planning, and formed the basis of "The Program" of modern socialism which Whitlam and the ALP presented to the voters in 1972.
Since 1918, Labor had called for the abolition of the existing Australian Constitution, and the vesting of all political power in Parliament, a plan which would turn the states into powerless geographic regions. Beginning in 1965, Whitlam sought to change this goal. He finally succeeded at the 1971 ALP Conference in Launceston, Tasmania
Launceston () or () is a city in the north of Tasmania, Australia, at the confluence of the North Esk and South Esk rivers where they become the Tamar River (kanamaluka). As of 2021, Launceston has a population of 87,645. Material was copied ...
, which called for Parliament to receive "such plenary powers as are necessary and desirable" to achieve the ALP's goals in domestic and international affairs. Labor also pledged to abolish the Senate; this goal was not erased from the party platform until 1979, after Whitlam had stepped down as leader.
Leader of the Opposition
 Soon after taking the leadership, Whitlam reorganised the ALP caucus, assigning portfolios and turning the Labor frontbench into a shadow cabinet. While the Liberal-Country Coalition had a huge majority in the House of Representatives, Whitlam energised the party by campaigning intensively to win two by-elections in 1967: first in Corio in Victoria, and later that year in Capricornia in Queensland. The November half-Senate election saw a moderate swing to Labor and against the Coalition, compared with the general election the previous year. These federal victories, in which both Whitlam and Holt campaigned, helped give Whitlam the leverage he needed to carry out party reforms.
At the end of 1967, Holt vanished while swimming in rough seas near Melbourne; his body was never recovered. John McEwen, as leader of the junior Coalition partner, the Country Party, took over as prime minister for three weeks until the Liberals could elect a new leader. Senator
Soon after taking the leadership, Whitlam reorganised the ALP caucus, assigning portfolios and turning the Labor frontbench into a shadow cabinet. While the Liberal-Country Coalition had a huge majority in the House of Representatives, Whitlam energised the party by campaigning intensively to win two by-elections in 1967: first in Corio in Victoria, and later that year in Capricornia in Queensland. The November half-Senate election saw a moderate swing to Labor and against the Coalition, compared with the general election the previous year. These federal victories, in which both Whitlam and Holt campaigned, helped give Whitlam the leverage he needed to carry out party reforms.
At the end of 1967, Holt vanished while swimming in rough seas near Melbourne; his body was never recovered. John McEwen, as leader of the junior Coalition partner, the Country Party, took over as prime minister for three weeks until the Liberals could elect a new leader. Senator John Gorton
Sir John Grey Gorton (9 September 1911 – 19 May 2002) was an Australian politician who served as the nineteenth Prime Minister of Australia, in office from 1968 to 1971. He led the Liberal Party during that time, having previously been a l ...
won the vote and became prime minister. The leadership campaign was conducted mostly by television, and Gorton appeared to have the visual appeal needed to keep Whitlam out of office. Gorton resigned his seat in the Senate, and in February 1968 won the by-election for Holt's seat of Higgins in Victoria. For the remainder of the year, Gorton appeared to have the better of Whitlam in the House of Representatives. In his chronicle of the Whitlam years, however, speechwriter Graham Freudenberg asserts that Gorton's erratic behaviour, Whitlam's strengthening of his party, and events outside Australia (such as the Vietnam War) ate away at Liberal dominance.
Gorton called an election for October 1969. Whitlam and the ALP, with little internal dissension, stood on a platform calling for domestic reform, an end to conscription, and the withdrawal of Australian troops from Vietnam by 1July 1970. Whitlam knew that, given the ALP's poor position after the 1966 election, victory was unlikely. Nevertheless, Whitlam scored an 18-seat swing, Labor's best performance since losing government in 1949. It also scored a 7.1 per cent two-party swing, the largest to not result in a change of government. Although the Coalition was returned for an eighth term in government, it was with a slim majority of three seats, down from 19 prior to the election. Labor actually won a bare majority of the two-party vote and only DLP preferences, especially in Melbourne-area seats, kept Whitlam from becoming prime minister. The 1970 half-Senate election brought little change to Coalition control, but the Coalition vote fell below 40 per cent for the first time, representing a severe threat to Gorton's leadership.
 In March 1971, the resentment against Gorton came to a head when a confidence vote in the Liberal caucus resulted in a tie. Declaring that this was a sign he no longer had the confidence of the party, Gorton resigned, and William McMahon was elected his successor. With the Liberals in turmoil, Whitlam and the ALP sought to gain public trust as a credible government-in-waiting. The party's actions, such as its abandonment of the White Australia policy, gained favourable media attention. The Labor leader flew to
In March 1971, the resentment against Gorton came to a head when a confidence vote in the Liberal caucus resulted in a tie. Declaring that this was a sign he no longer had the confidence of the party, Gorton resigned, and William McMahon was elected his successor. With the Liberals in turmoil, Whitlam and the ALP sought to gain public trust as a credible government-in-waiting. The party's actions, such as its abandonment of the White Australia policy, gained favourable media attention. The Labor leader flew to Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
and pledged himself to the independence of what was then under Australian trusteeship. In 1971, Whitlam flew to Beijing and met with Chinese officials, including Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai (; 5 March 1898 – 8 January 1976) was a Chinese statesman and military officer who served as the first Premier of the People's Republic of China, premier of the People's Republic of China from 1 October 1949 until his death on 8 J ...
. McMahon attacked Whitlam for the visit and claimed that the Chinese had manipulated him. This attack backfired when US President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
announced that he would visit China the following year. His National Security Advisor A national security advisor serves as the chief advisor to a national government on matters of security. The advisor is not usually a member of the government's cabinet but is usually a member of various military or security councils.
National sec ...
, Henry Kissinger
Henry Alfred Kissinger (; ; born Heinz Alfred Kissinger, May 27, 1923) is a German-born American politician, diplomat, and geopolitical consultant who served as United States Secretary of State and National Security Advisor under the presid ...
, visited Beijing between 9–11 July (less than a week after Whitlam's visit of 4–6 July), and, unknown to Whitlam, some of Kissinger's staff had been in Beijing preparing for Kissinger's visit at the same time as the Labor delegation. According to Whitlam biographer Jenny Hocking, the incident transformed Whitlam into an international statesman, while McMahon was seen as reacting defensively to Whitlam's foreign policy ventures. Other errors by McMahon, such as a confused ad-lib speech while visiting Washington, and a statement to Indonesia's President Suharto
Suharto (; ; 8 June 1921 – 27 January 2008) was an Indonesian army officer and politician, who served as the second and the longest serving president of Indonesia. Widely regarded as a military dictator by international observers, Suharto ...
that Australia was a "west European nation", also damaged the government.
 By early 1972, Labor had established a clear lead in the polls; indeed, for the first time since 1955 its support was greater than the combined vote for the Coalition and DLP. Unemployment was at a ten-year peak, rising to 2.14 per cent in August (though the unemployment rate was calculated differently compared to the present, and did not include thousands of rural workers on Commonwealth-financed relief work). Inflation was also at its highest rate since the early 1950s. The government recovered slightly in the August Budget session of Parliament, proposing income tax cuts and increased spending. The Labor strategy for the run-up to the election was to sit back and allow the Coalition to make mistakes. Whitlam controversially stated in March "draft-dodging is not a crime" and that he would be open to a revaluation of the Australian dollar. With the Coalition sinking in the polls and his own personal approval ratings down as low as 28 per cent, McMahon waited as long as he could, finally calling an election for the House of Representatives for 2December. Whitlam noted that the polling day was the anniversary of the
By early 1972, Labor had established a clear lead in the polls; indeed, for the first time since 1955 its support was greater than the combined vote for the Coalition and DLP. Unemployment was at a ten-year peak, rising to 2.14 per cent in August (though the unemployment rate was calculated differently compared to the present, and did not include thousands of rural workers on Commonwealth-financed relief work). Inflation was also at its highest rate since the early 1950s. The government recovered slightly in the August Budget session of Parliament, proposing income tax cuts and increased spending. The Labor strategy for the run-up to the election was to sit back and allow the Coalition to make mistakes. Whitlam controversially stated in March "draft-dodging is not a crime" and that he would be open to a revaluation of the Australian dollar. With the Coalition sinking in the polls and his own personal approval ratings down as low as 28 per cent, McMahon waited as long as he could, finally calling an election for the House of Representatives for 2December. Whitlam noted that the polling day was the anniversary of the Battle of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz in ...
at which another "ramshackle, reactionary coalition" had been given a "crushing defeat".
Labor campaigned under the slogan " It's Time", an echo of Menzies' successful 1949 slogan, "It's Time for a Change". Surveys showed that even Liberal voters approved of the Labor slogan. Whitlam pledged an end to conscription and the release of individuals who had refused the draft; an income tax surcharge to pay for universal health insurance; free dental care for students; and renovation of ageing urban infrastructure. The party pledged to eliminate university tuition fees and establish a schools commission to evaluate educational needs. The party benefited from the support of the proprietor of News Limited
News Corp Australia is an Australian media conglomerate and wholly owned subsidiary of the American News Corp. One of Australia's largest media conglomerates, News Corp Australia employs more than 8,000 staff nationwide and approximately 3,0 ...
, Rupert Murdoch
Keith Rupert Murdoch ( ; born 11 March 1931) is an Australian-born American business magnate. Through his company News Corp, he is the owner of hundreds of local, national, and international publishing outlets around the world, including ...
, who preferred Whitlam over McMahon. Labor was so dominant in the campaign that some of Whitlam's advisers urged him to stop joking about McMahon; people were feeling sorry for him. The election saw the ALP increase its tally by 12 seats, mostly in suburban Sydney and Melbourne, for a majority of nine in the House of Representatives. The ALP gained little beyond the suburban belts, however, losing a seat in South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
and two in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
.
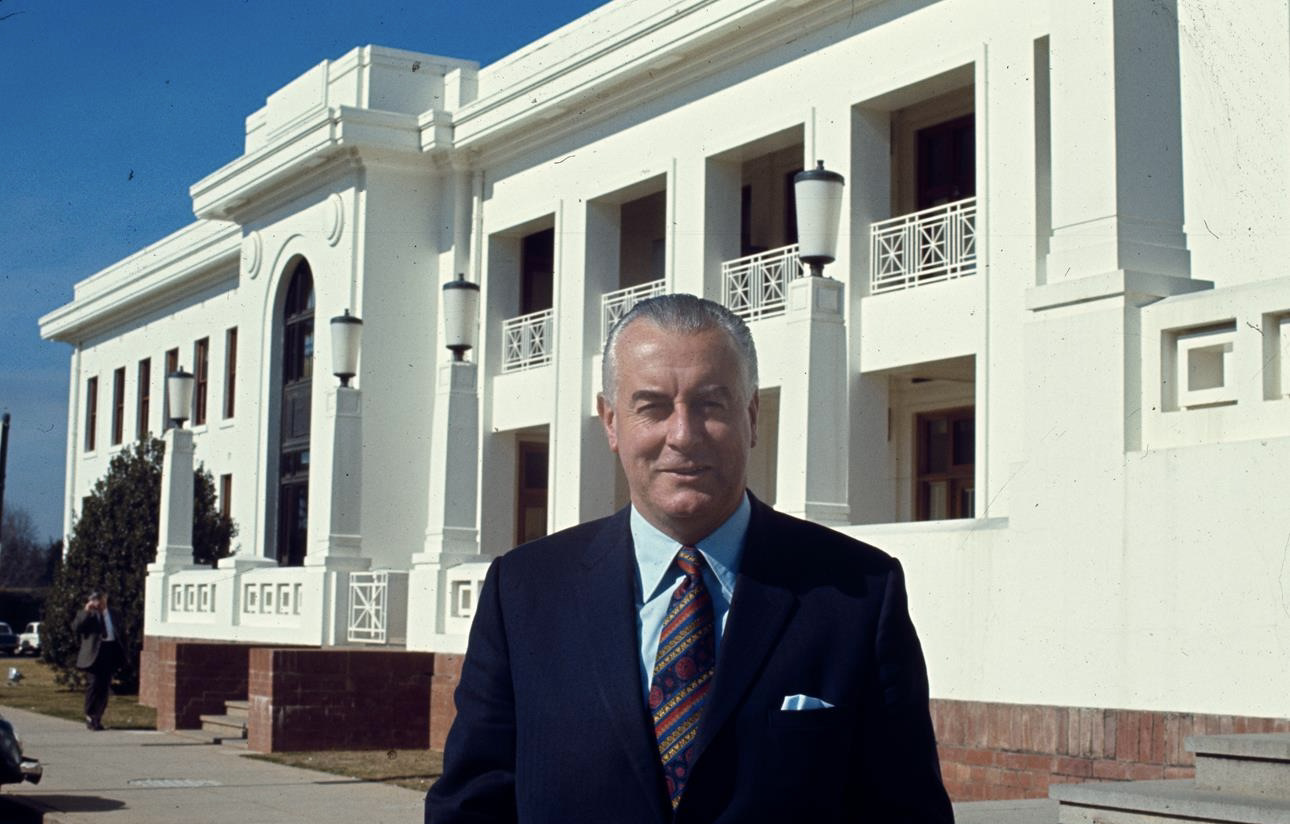
Prime Minister, 1972–1975
First term
Duumvirate
 Whitlam took office with a majority in the House of Representatives, but without control of the Senate (elected in the 1967 and 1970 half-elections). The Senate at that time consisted of ten members from each of the six states, elected by
Whitlam took office with a majority in the House of Representatives, but without control of the Senate (elected in the 1967 and 1970 half-elections). The Senate at that time consisted of ten members from each of the six states, elected by single transferable vote
Single transferable vote (STV) is a multi-winner electoral system in which voters cast a single vote in the form of a ranked-choice ballot. Voters have the option to rank candidates, and their vote may be transferred according to alternate p ...
. Historically, when Labor won government, the parliamentary caucus chose the ministers, with the party leader having the power only to assign portfolios. However, the new Labor caucus would not meet until after the final results came in on 15 December.
With Labor's win beyond doubt even though counting was still underway, McMahon advised the Governor-General, Sir Paul Hasluck, that he was no longer in a position to govern. Soon afterward, Whitlam advised Hasluck that he could form a government with his new majority. This was in accordance with longstanding Australian constitutional practice. Convention also held that McMahon would stay on as caretaker prime minister until the full results were in. However, Whitlam was unwilling to wait that long. On 5December, per Whitlam's request, Hasluck swore Whitlam and Labor's deputy leader, Lance Barnard
Lance Herbert Barnard AO (1 May 19196 August 1997) was an Australian politician and diplomat. He was the deputy leader of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) from 1967 to 1974 and held senior ministerial office in the Whitlam Government, most no ...
, as an interim two-man government, with Whitlam as prime minister and Barnard as deputy prime minister. The two men held 27 portfolios during the two weeks before a full cabinet could be determined.
During the two weeks the so-called "duumvirate
Diarchy (from Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally misspelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate (from Latin ', "the office of ...
" held office, Whitlam sought to fulfill those campaign promises that did not require legislation. Whitlam ordered negotiations to establish full relations with the People's Republic of China, and broke those with Taiwan. The diplomatic relations were established in 1972 and an embassy opened in Beijing in 1973. Legislation allowed the defence minister to grant exemptions from conscription. Barnard held this office, and exempted everyone. Seven men were at that time incarcerated for refusing conscription; Whitlam arranged for their liberation. The Whitlam government in its first days reopened the equal pay case pending before the Commonwealth Conciliation and Arbitration Commission
The Australian Industrial Relations Commission (AIRC), known from 1956 to 1973 as the Commonwealth Conciliation and Arbitration Commission and from 1973 to 1988 as the Australian Conciliation and Arbitration Commission, was a tribunal with powers ...
, and appointed a woman, Elizabeth Evatt
Elizabeth Andreas Evatt (born 11 November 1933), an eminent Australian reformist lawyer and jurist who sat on numerous national and international tribunals and commissions, was the first Chief Justice of the Family Court of Australia, the fi ...
, to the commission. Whitlam and Barnard eliminated sales tax on contraceptive pills, announced major grants for the arts, and appointed an interim schools commission. The duumvirate barred racially discriminatory sports teams from Australia, and instructed the Australian delegation at the United Nations to vote in favour of sanctions on apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
South Africa and Rhodesia
Rhodesia (, ), officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was an unrecognised state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the ''de facto'' successor state to the British colony of S ...
. It also ordered the Australian Army Training Team home from Vietnam, ending Australia's involvement in the war; most troops, including all conscripts, had been withdrawn by McMahon. According to Whitlam's speechwriter Graham Freudenberg, the duumvirate was a success, as it showed that the Labor government could manipulate the machinery of government, despite almost a quarter-century in opposition. However, Freudenberg noted that the rapid pace and public excitement caused by the duumvirate's actions caused the Opposition to be wary of giving Labor too easy a time, and gave rise to one post-mortem assessment of the Whitlam government: "We did too much too soon."
Enacting a program
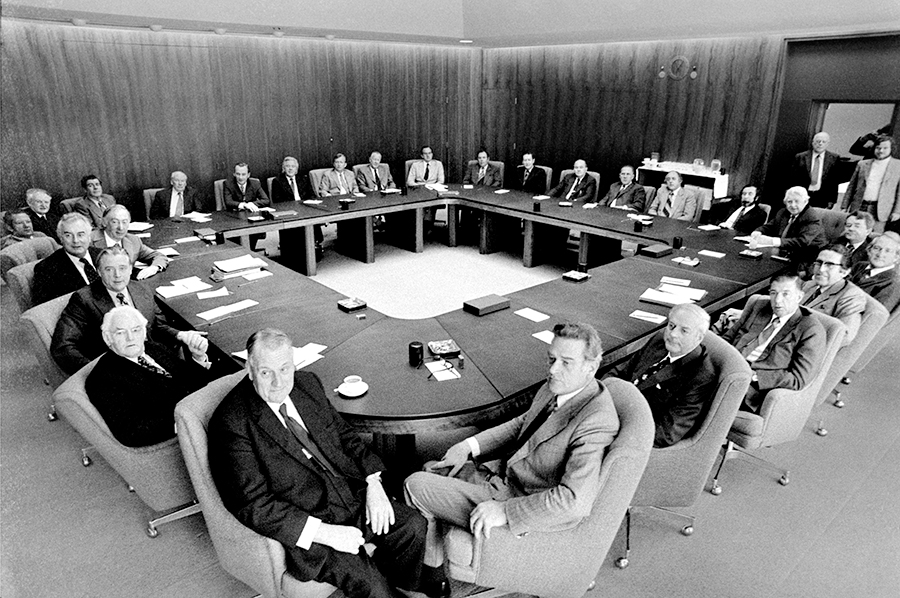
 The McMahon government had consisted of 27 ministers, twelve of whom comprised the Cabinet. In the run-up to the election, the Labor caucus had decided that if the party took power all 27 ministers were to be Cabinet members. Intense canvassing took place amongst ALP parliamentarians as the duumvirate did its work, and on 18 December the caucus elected the Cabinet. The results were generally acceptable to Whitlam, and within three hours, he had announced the portfolios of the Cabinet members. To give himself greater control over the Cabinet, in January 1973 Whitlam established five Cabinet committees (with the members appointed by himself, not the caucus) and took full control of the Cabinet agenda.
Whitlam, prime minister for fewer than three years between 1972 and 1975, pushed through a raft of reforms that radically changed Australia's economic, legal and cultural landscape.
The Whitlam government abolished the death penalty for federal crimes.
The McMahon government had consisted of 27 ministers, twelve of whom comprised the Cabinet. In the run-up to the election, the Labor caucus had decided that if the party took power all 27 ministers were to be Cabinet members. Intense canvassing took place amongst ALP parliamentarians as the duumvirate did its work, and on 18 December the caucus elected the Cabinet. The results were generally acceptable to Whitlam, and within three hours, he had announced the portfolios of the Cabinet members. To give himself greater control over the Cabinet, in January 1973 Whitlam established five Cabinet committees (with the members appointed by himself, not the caucus) and took full control of the Cabinet agenda.
Whitlam, prime minister for fewer than three years between 1972 and 1975, pushed through a raft of reforms that radically changed Australia's economic, legal and cultural landscape.
The Whitlam government abolished the death penalty for federal crimes. Legal aid
Legal aid is the provision of assistance to people who are unable to afford legal representation and access to the court system. Legal aid is regarded as central in providing access to justice by ensuring equality before the law, the right to co ...
was established, with offices in each state capital. It abolished university
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
fees, and established the Schools Commission to allocate funds to schools. Whitlam founded the Department of Urban Development and, having lived in developing Cabramatta, most of which lacked sewage facilities, established the National Sewerage Program
The National Sewerage Program was an Australian federal program under the Whitlam and Fraser governments established to provide funding for the expansion of municipal sewerage systems. At the time Australia was lagging behind other developed nati ...
, which set a goal to leave no urban home unsewered. The Whitlam government gave grants directly to local government units for urban renewal, flood prevention, and the promotion of tourism. Other federal grants financed highways linking the state capitals, and paid for standard-gauge rail lines between the states. The government attempted to set up a new city at Albury–Wodonga
Albury–Wodonga is the broad settlement incorporating the twin Australian cities of Albury and Wodonga, which are separated geographically by the Murray River and politically by a state border: Albury on the north of the river is part of New So ...
on the Victoria–New South Wales border. The process was started for "Advance Australia Fair
"Advance Australia Fair" is the national anthem of Australia. Written by Scottish people, Scottish-born composer Peter Dodds McCormick, the song was first performed in 1878, sung in Australia as a patriotic song. It first replaced "God Save the ...
" to become the country's national anthem in place of "God Save the Queen
"God Save the King" is the national and/or royal anthem of the United Kingdom, most of the Commonwealth realms, their territories, and the British Crown Dependencies. The author of the tune is unknown and it may originate in plainchant, bu ...
". The Order of Australia
The Order of Australia is an honour that recognises Australian citizens and other persons for outstanding achievement and service. It was established on 14 February 1975 by Elizabeth II, Queen of Australia, on the advice of the Australian Gove ...
replaced the British honours system in early 1975.
In 1973, the National Gallery of Australia
The National Gallery of Australia (NGA), formerly the Australian National Gallery, is the national art museum of Australia as well as one of the largest art museums in Australia, holding more than 166,000 works of art. Located in Canberra in th ...
, then called the Australian National Gallery, bought the painting "Blue Poles
''Blue Poles'', also known as ''Number 11, 1952'' is an abstract expressionist painting by American artist Jackson Pollock. It was purchased amid controversy by the National Gallery of Australia in 1973 and today remains one of the gallery's ma ...
" by contemporary artist Jackson Pollock
Paul Jackson Pollock (; January 28, 1912August 11, 1956) was an American painter and a major figure in the abstract expressionist movement. He was widely noticed for his " drip technique" of pouring or splashing liquid household paint onto a hor ...
for US$2million (A$1.3million at the time of payment), which was about a third of its annual budget. This required Whitlam's personal permission, which he gave on the condition the price was publicised. The purchase created a political and media scandal, and was said to symbolise, alternatively, Whitlam's foresight and vision or his profligate spending.
Whitlam travelled extensively as prime minister, and was the first Australian prime minister to visit China while in office. He was criticised for making this visit, especially after Cyclone Tracy
Cyclone Tracy was a tropical cyclone that devastated the city of Darwin, Northern Territory, Australia, from 24 to 26 December 1974. The small, developing easterly storm had been observed passing clear of the city initially, but then turned t ...
struck Darwin; he interrupted an extensive tour of Europe for 48 hours (deemed too brief a period by many) to view the devastation.

Early troubles
From the start of the Whitlam government, the Opposition, led by Billy Snedden, who replaced McMahon as Liberal leader in December 1972, sought to use control of the Senate to baulk Whitlam. It did not seek to block all government legislation; the Coalition senators, led by Senate Liberal leaderReg Withers
Reginald Greive Withers (26 October 1924 – 15 November 2014) was a long-serving member of the Australian Senate, a government minister, and Lord Mayor of Perth.
Early life
Withers was born in Bunbury, Western Australia. Withers was the son o ...
, sought to block government legislation only when the obstruction would advance the Opposition's agenda. The Whitlam government also had troubles in relations with the states. New South Wales refused the government's request to close the Rhodesian Information Centre in Sydney. The Queensland premier, Joh Bjelke-Petersen
Sir Johannes Bjelke-Petersen (13 January 191123 April 2005), known as Joh Bjelke-Petersen, was a conservative Australian politician. He was the longest-serving and longest-lived premier of Queensland, holding office from 1968 to 1987, during ...
refused to consider any adjustment in Queensland's border with Papua New Guinea, which, due to the state's ownership of islands in the Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
, came within half a kilometre of the Papuan mainland. Liberal state governments in New South Wales and Victoria were re-elected by large margins in 1973. Whitlam and his majority in the House of Representatives proposed a constitutional referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
in December 1973, transferring control of wages and prices from the states to the federal government. The two propositions failed to attract a majority of voters in any state, and were rejected by over 800,000 votes nationwide.
In 1974, the Senate refused to pass six bills after they were passed twice by the House of Representatives. With the Opposition threatening to disrupt money supply
Supply may refer to:
*The amount of a resource that is available
**Supply (economics), the amount of a product which is available to customers
**Materiel, the goods and equipment for a military unit to fulfill its mission
*Supply, as in confidenc ...
to government, Whitlam used the Senate's recalcitrance to trigger a double dissolution
A double dissolution is a procedure permitted under the Australian Constitution to resolve deadlocks in the bicameral Parliament of Australia between the House of Representatives (lower house) and the Senate (upper house). A double dissolution ...
election, holding it instead of the half-Senate election. After a campaign featuring the Labor slogan "Give Gough a fair go", the Whitlam government was returned, with its majority in the House of Representatives cut from seven to five and its Senate seats increased by three. It was only the second time since Federation that a Labor government had been elected to a second full term. The government and the opposition each had 29 Senators with two seats held by independents. The deadlock over the twice-rejected bills was broken, uniquely in Australian history, with a special
Special or specials may refer to:
Policing
* Specials, Ulster Special Constabulary, the Northern Ireland police force
* Specials, Special Constable, an auxiliary, volunteer, or temporary; police worker or police officer
Literature
* ''Specia ...
joint sitting
A joint session or joint convention is, most broadly, when two normally separate decision-making groups meet, often in a special session or other extraordinary meeting, for a specific purpose.
Most often it refers to when both houses of a bicamer ...
of the two houses of Parliament under Section 57 of the Constitution. This session, authorised by the new governor-general, John Kerr, passed bills providing for universal health insurance (known then as Medibank, today as Medicare) and providing the Northern Territory and Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding townships. ...
with representation in the Senate, effective at the next election.
Murphy raids
 In February 1973, the Attorney General, Senator
In February 1973, the Attorney General, Senator Lionel Murphy
Lionel Keith Murphy QC (30 August 1922 – 21 October 1986) was an Australian politician, barrister, and judge. He was a Senator for New South Wales from 1962 to 1975, serving as Attorney-General in the Whitlam Government, and then sat on the ...
, led a police raid on the Melbourne office of the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation
The Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO ) is Australia's national security agency responsible for the protection of the country and its citizens from espionage, sabotage, acts of foreign interference, politically motivated vio ...
, which was under his ministerial responsibility. Murphy believed that ASIO might have files relating to threats against Yugoslav Prime Minister Džemal Bijedić, who was about to visit Australia, and feared ASIO might conceal or destroy them. The Opposition attacked the Government over the raid, terming Murphy a "loose cannon". A Senate investigation of the incident was cut short when Parliament was dissolved in 1974. According to journalist and author Wallace Brown, the controversy over the raid continued to dog the Whitlam government throughout its term, because the incident was "so silly".
Gair Affair
By early 1974, the Senate had rejected nineteen government bills, ten of them twice. With a half-Senate election due by mid-year, Whitlam looked for ways to shore up support in that body. Queensland senator and former DLP leaderVince Gair
Vincent Clair Gair (25 February 190111 November 1980) was an Australian politician. He served as Premier of Queensland from 1952 until 1957, when his stormy relations with the trade union movement saw him expelled from the Labor Party. He was e ...
signalled his willingness to leave the Senate for a diplomatic post. Gair's term would not expire until the following half-Senate election or upon a double dissolution election. With five Queensland seats at stake in the half-Senate election, the ALP was expected to win only two, but if six (including Gair's) were at stake, the party would be likely to win a third. Possible control of the Senate was therefore at stake; Whitlam agreed to Gair's request and had Governor-General Sir Paul Hasluck appoint him ambassador to Ireland. Word leaked of Gair's pending resignation, and Whitlam's opponents attempted to counteract his manoeuvre. On what became known as the "Night of the Long Prawns", Country Party members secreted Gair at a small party in a legislative office as the ALP searched for him to secure his written resignation. As Gair enjoyed beer and prawns, Bjelke-Petersen advised the Queensland governor, Colin Hannah
Air Marshal Sir Colin Thomas Hannah, (22 December 1914 – 22 May 1978) was a senior commander in the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) and a Governor of Queensland. Born in Western Australia, he was a member of the Militia before joining the ...
, to issue writs for only the usual five vacancies, since Gair's seat was not yet vacant, effectively countering Whitlam's plan.
Second term
By mid-1974, Australia was in an economic slump, suffering from the1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
and 1973–75 recession. The 1973 oil crisis had caused prices to spike and, according to government figures, inflation topped 13 per cent for over a year between 1973 and 1974. Part of the inflation was due to Whitlam's desire to increase wages and conditions of the Commonwealth Public Service as a pacesetter for the private sector. The Whitlam government had cut tariffs by 25 per cent in 1973; 1974 saw an increase in imports of 30 per cent and a $1.5billion increase in the trade deficit
The balance of trade, commercial balance, or net exports (sometimes symbolized as NX), is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balance ...
. Primary producers of commodities such as beef were caught in a credit squeeze as short-term rates rose to extremely high levels. Unemployment also rose significantly. Unease within the ALP led to Barnard's defeat when Jim Cairns challenged him for his deputy leadership. Whitlam gave little help to his embattled deputy, who had formed the other half of the duumvirate.
Despite these economic indicators, the Budget presented in August 1974 saw large increases in spending, especially in education. Treasury officials had advised a series of tax and fee increases, ranging from excise taxes to the cost of posting a letter; their advice was mostly rejected by Cabinet. The Budget was unsuccessful in dealing with the inflation and unemployment, and Whitlam introduced large tax cuts in November. He also announced additional spending to help the private sector.
Beginning in October 1974, the Whitlam government sought overseas loans to finance its development plans, with the newly enriched oil nations a likely target. Whitlam attempted to secure financing before informing the Loan Council which included state officials hostile to Whitlam. His government empowered Pakistani financier Tirath Khemlani as an intermediary in the hope of securing US$4billion in loans. While the Loans Affair did not result in a loan, according to author and Whitlam speechwriter Graham Freudenberg, "The only cost involved was the cost to the reputation of the Government. That cost was to be immenseit was government itself."
Whitlam appointed Senator Murphy to the High Court, even though Murphy's Senate seat would not be up for election if a half-Senate election were held. Labor then held three of the five short-term New South Wales Senate seats. Under proportional representation, Labor could hold its three short-term seats in the next half-Senate election but, if Murphy's seat were also contested, Labor was unlikely to win four out of six. Thus, a Murphy appointment meant the almost certain loss of a seat in the closely divided Senate at the next election. Whitlam appointed Murphy anyway. By convention, senators appointed by the state legislature to fill casual vacancies were from the same political party as the former senator. The New South Wales premier, Tom Lewis felt that this convention applied only to vacancies caused by deaths or ill-health, and arranged for the legislature to elect Cleaver Bunton
Cleaver Ernest Bunton (5 May 190220 January 1999) was a long-serving Mayor of Albury, New South Wales, Australia, who came to national prominence in 1975 when he was controversially appointed to the Senate by New South Wales Liberal Party Premi ...
, former mayor of Albury
Albury () is a major regional city in New South Wales, Australia. It is located on the Hume Highway and the northern side of the Murray River. Albury is the seat of local government for the council area which also bears the city's name – the ...
and an independent. By March 1975, many Liberal parliamentarians felt Snedden was doing an inadequate job as leader of the Opposition, and that Whitlam was dominating him in the House of Representatives. Malcolm Fraser
John Malcolm Fraser (; 21 May 1930 – 20 March 2015) was an Australian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Australia from 1975 to 1983, holding office as the leader of the Liberal Party of Australia.
Fraser was raised on hi ...
challenged Snedden for the leadership, and defeated him on 21 March.
Soon after Fraser's accession, controversy arose over the Whitlam government's actions in trying to restart peace talks in Vietnam. As the North prepared to end the civil war, Whitlam sent cables to both Vietnamese governments, telling Parliament both cables were substantially the same. The Opposition contended he had misled Parliament, and a motion to censure Whitlam was defeated along party lines. The Opposition also attacked Whitlam for not allowing enough South Vietnamese refugees into Australia, with Fraser calling for the entry of 50,000. Freudenberg alleges that 1,026 Vietnamese refugees entered Australia in the final eight months of the Whitlam government, and only 399 in 1976 under Fraser. However, by 1977, Australia had accepted more than five thousand refugees.
As the political situation deteriorated, Whitlam and his government continued to enact legislation: The Family Law Act 1975
The ''Family Law Act 1975'' (Cth) is an Act of the Parliament of Australia. It has 15 parts and is the primary piece of legislation dealing with divorce, parenting arrangements between separated parents (whether married or not), property separ ...
provided for no-fault divorce while the Racial Discrimination Act 1975
The ''Racial Discrimination Act 1975'' (Cth). is an Act of the Australian Parliament, which was enacted on 11 June 1975 and passed by the Whitlam government. The Act makes racial discrimination in certain contexts unlawful in Australia, and al ...
caused Australia to ratify the International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination
The International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (ICERD) is a United Nations convention. A third -generation human rights instrument, the Convention commits its members to the elimination of racial discri ...
that Australia had signed under Holt, but which had never been ratified. In August 1975, Whitlam gave the Gurindji people
The Gurindji are an Aboriginal Australian people of northern Australia, southwest of Katherine in the Northern Territory's Victoria River region.
Language and culture
Gurindji is one of the eastern Ngumbin languages, in the Ngumbin-Yapa s ...
of the Northern Territory title deeds to part of their traditional lands, beginning the process of Aboriginal land reform. The next month, Australia granted independence to Papua New Guinea.
Carnation Revolution
The Carnation Revolution ( pt, Revolução dos Cravos), also known as the 25 April ( pt, 25 de Abril, links=no), was a military coup by left-leaning military officers that overthrew the authoritarian Estado Novo regime on 25 April 1974 in Lisbo ...
, Portugal began a process of decolonisation and began a withdrawal from Portuguese Timor
Portuguese Timor ( pt, Timor Português) was a colonial possession of Portugal that existed between 1702 and 1975. During most of this period, Portugal shared the island of Timor with the Dutch East Indies.
The first Europeans to arrive in the ...
(later East Timor
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-weste ...
). Australians had long taken an interest in the colony; the nation had sent troops to the region during World WarII, and many East Timorese had fought the Japanese as guerrillas. In September 1974, Whitlam met with President Suharto in Indonesia and indicated that he would support Indonesia if it annexed East Timor. At the height of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, and in the context of the American retreat from Indo-China, he felt that incorporation of East Timor into Indonesia would enhance the stability of the region, and reduce the risk of the East Timorese FRETILIN
The Revolutionary Front for an Independent East Timor ( pt, Frente Revolucionária de Timor-Leste Independente, abbreviated as Fretilin) is a centre-left political party in East Timor. They presently hold 23 of 65 seats in the National Parliam ...
movement, which many feared was communist, coming to power.
Whitlam had offered Barnard a diplomatic post and in early 1975 Barnard agreed to this, triggering a by-election
A by-election, also known as a special election in the United States and the Philippines, a bye-election in Ireland, a bypoll in India, or a Zimni election (Urdu: ضمنی انتخاب, supplementary election) in Pakistan, is an election used to f ...
in his Tasmanian electorate of Bass. The election on 28 June proved a disaster for Labor, which lost the seat with a swing against it of 17 per cent. The next week, Whitlam removed deputy prime minister Cairns, who had misled Parliament about the Loans Affair amid controversy about his relationship with his office manager, Junie Morosi
Junie Morosi (born 26 July 1933) is an Australian businesswoman, who became a public figure in the 1970s through her relationship with Jim Cairns, Deputy Prime Minister in the Whitlam Labor government. Morosi's appointment as Cairns's principal ...
. At the time of Cairns's dismissal, one Senate seat was vacant, following the death on 30 June of Queensland ALP Senator Bertie Milliner
Bertie ("Bert") Richard Milliner (17 July 1911 – 30 June 1975) was an Australian trade unionist, politician and Senator, representing the Australian Labor Party (ALP). He would have been a minor figure in Australia's political history but for ...
. The state Labor party nominated Mal Colston
Malcolm Arthur Colston (5 April 1938 – 23 August 2003) was an Australian politician who served as a Senator for Queensland from 1975 to 1999. He was a member of the Labor Party until 1996, when he resigned to sit as an independent followi ...
, resulting in a deadlock. The unicameral Queensland legislature twice voted against Colston, and the party refused to submit any alternative candidates. Bjelke-Petersen finally convinced the legislature to elect a low-level union official, Albert Field
Albert Patrick Field (11 October 19101 July 1990) was an Australian Labor Party member. In 1975 he was chosen as a Senator in unusual circumstances that played a significant role in precipitating the 1975 Australian constitutional crisis. Gou ...
, who had contacted his office and expressed a willingness to serve. In interviews, Field made it clear he would not support Whitlam. Field was expelled from the ALP for standing against Colston, and Labor senators boycotted his swearing-in. Whitlam argued that, because of the manner of filling vacancies, the Senate was "corrupted" and "tainted", with the Opposition enjoying a majority they did not win at the ballot box.
Dismissal
In October 1975, the Opposition, led by Malcolm Fraser, determined to withhold supply by deferring consideration of appropriation bills. With Field on leave (his Senate appointment having been challenged), the Coalition had an effective majority of 30–29 in the Senate. The Coalition believed that if Whitlam could not deliver supply, and would not advise new elections, Kerr would have to dismiss him. Supply would run out on 30 November. The stakes were raised in the conflict on 10 October, when the High Court declared valid the Act granting the territories two senators each. In a half-Senate election, most successful candidates would not take their places until 1July 1976, but the territories' senators, and those filling Field's and Bunton's seats, would assume their seats immediately. This gave Labor an outside chance of controlling the Senate, at least until 1July 1976. On 14 October, Labor ministerRex Connor
Reginald Francis Xavier "Rex" Connor (26 January 190722 August 1977) was an Australian politician who served as a member of the House of Representatives from 1963 to his death, representing the Labor Party. He was the Minister for Minerals ...
, mastermind of the loans scheme, was forced to resign when Khemlani released documents showing that Connor had made misleading statements. The continuing scandal bolstered the Coalition in their stance that they would not concede supply. Whitlam on the other hand, convinced that he would win the battle, was glad of the distraction from the Loans Affair, and believed he would "smash" not only the Senate, but Fraser's leadership as well.
Whitlam told the House of Representatives on 21 October,
Whitlam and his ministers repeatedly claimed that the Opposition was damaging not only the constitution, but the economy as well. The Coalition senators remained united, though several became increasingly concerned about the tactic of blocking supply. As the crisis dragged into November, Whitlam attempted to make arrangements for public servants and suppliers to be able to cash cheques at banks. These transactions would be temporary loans which the government would repay once supply was restored. This plan to prolong government without supply was presented to Kerr unsigned on 6November, under the title "Draft Joint Opinion" (ostensibly of solicitor-general Maurice Byers
Sir Maurice Hearne Byers (10 November 191717 January 1999) was a noted Australian jurist and constitutional expert. He was the Commonwealth Solicitor-General from 1973 to 1983, in which capacity he played a role in the Gair Affair and the 197 ...
and attorney-general Kep Enderby
Keppel Earl Enderby (25 June 1926 – 7 January 2015) was an Australian politician and judge. Enderby was a member of the House of Representatives, representing the Australian Labor Party between 1970 and 1975 and became a senior cabinet minist ...
). It proposed that public employees, including members of the armed forces and police, "could assign arrears of pay by way of mortgage". The government's refusal to formalise this and other "advice" was a factor justifying Kerr's resort to advice from elsewhere.
Kerr was following the crisis closely. At a luncheon with Whitlam and several of his ministers on 30 October, Kerr suggested a compromise: if Fraser conceded supply, Whitlam would agree not to call the half-Senate election until May or June 1976, or alternatively would agree not to call the Senate into session until after 1July. Whitlam rejected the idea, seeking to end the Senate's right to deny supply. On 3November, after a meeting with Kerr, Fraser proposed that if the government agreed to hold a House of Representatives election at the same time as the half-Senate election, the Coalition would concede supply. Whitlam rejected this offer, stating that he had no intention of advising a House election for at least a year.
With the crisis unresolved, Kerr decided to dismiss Whitlam as prime minister. Fearing that Whitlam would go to the Queen
In the English-speaking world, The Queen most commonly refers to:
* Elizabeth II (1926–2022), Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 1952 until her death
The Queen may also refer to:
* Camilla, Queen Consort (born 1947), ...
and potentially have him removed, the Governor-General gave Whitlam no prior hint. Against Whitlam's advice, he conferred with High Court Chief Justice Sir Garfield Barwick, who agreed that he had the power to dismiss Whitlam.
A meeting among the party leaders, including Whitlam and Fraser, to resolve the crisis on the morning of 11 November came to nothing. Kerr and Whitlam met at the Governor-General's office that afternoon at 1:00pm. Unknown to Whitlam, Fraser was waiting in an ante-room; Whitlam later said he would not have set foot in the building if he had known Fraser was there. Whitlam, as he had told Kerr by phone earlier that day, came prepared to advise a half-Senate election, to be held on 13 December. Kerr instead told Whitlam he had terminated his commission as prime minister, and handed him a letter to that effect. After the conversation, Whitlam returned to the Prime Minister's residence, The Lodge, had lunch and conferred with his advisers. Immediately after his meeting with Whitlam, Kerr commissioned Fraser as caretaker Prime Minister, on the assurance he could obtain supply and would then advise Kerr to dissolve both houses for election.
In the confusion, Whitlam and his advisers did not immediately tell any Senate members of the dismissal, with the result that when the Senate convened at 2:00pm, the appropriation bills were rapidly passed, with the ALP senators assuming the Opposition had given in. The bills were soon sent to Kerr to receive Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in other ...
. At 2:34pm, ten minutes after supply had been secured, Fraser rose in the House and announced he was prime minister. Whitlam immediately moved a successful no confidence motion against Fraser in the House. The Speaker, Gordon Scholes, was instructed to advise Kerr to reinstate Whitlam.
Kerr refused to receive Scholes, keeping him waiting for more than an hour. In that time Kerr rang Justice Anthony Mason to ask for advice. Mason told him the no confidence motion in the House was "irrelevant". Kerr then prorogued Parliament by proclamation: his Official Secretary, David Smith, came to Parliament House to proclaim the dissolution from the front steps. A large, angry crowd had gathered, and Smith was nearly drowned out by their noise. He concluded his task by taking the unilateral step of re-instating the traditional ending for a royal proclamation "God save the Queen", a practice the Whitlam government had abolished. Whitlam, who had been standing behind Smith, then addressed the crowd:
Well may we say "God save the Queen", because nothing will save the Governor-General! The Proclamation which you have just heard read by the Governor-General's Official Secretary was countersigned Malcolm Fraser, who will undoubtedly go down in Australian history from Remembrance Day 1975 as Kerr's cur. They won't silence the outskirts of Parliament House, even if the inside has been silenced for a few weeks.... Maintain your rage and enthusiasm for the campaign for the election now to be held and until polling day.
Alleged CIA involvement
During the crisis, Whitlam had alleged thatNational Country Party
The National Party of Australia, also known as The Nationals or The Nats, is an Australian political party. Traditionally representing graziers, farmers, and regional voters generally, it began as the Australian Country Party in 1920 at a fe ...
leader Doug Anthony
John Douglas Anthony, (31 December 192920 December 2020) was an Australian politician. He served as leader of the National Party of Australia from 1971 to 1984 and was the second and longest-serving Deputy Prime Minister, holding the position ...
had close links to the US Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
(CIA). In early November 1975, the ''Australian Financial Review
''The Australian Financial Review'' (abbreviated to the ''AFR'') is an Australian business-focused, compact daily newspaper covering the current business and economic affairs of Australia and the world. The newspaper is based in Sydney, New Sou ...
'' wrote that Richard Lee Stallings, a former CIA officer, had been channelling money to Anthony, who was a close friend.
Kerr had been involved with a number of CIA fronts. In the 1950s, Kerr had joined the Association for Cultural Freedom, a conservative group which had been established by, and received funding from, the CIA through the Congress for Cultural Freedom
The Congress for Cultural Freedom (CCF) was an anti-communist advocacy group founded in 1950. At its height, the CCF was active in thirty-five countries. In 1966 it was revealed that the CIA was instrumental in the establishment and funding of the ...
. Kerr was on its executive board and wrote for its magazine '' Quadrant''. In 1966, Kerr helped to found Lawasia (or Law Asia), an organization of lawyers which had offices in all the major capitals of Asia. It was funded by The Asia Foundation
The Asia Foundation is a nonprofit international development organization committed to "improving lives across a dynamic and developing Asia". The Asia Foundation (TAF) was established in 1954 to undertake cultural and educational activities on be ...
, a prominent CIA front.
Christopher Boyce
Christopher John Boyce (born 16 February 1953) is a former American defense industry employee who was convicted of selling United States spy satellite secrets to the Soviet Union in the 1970s.
Early life
Boyce is the son of Noreen Boyce (née H ...
, who was convicted of spying for the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
while an employee of a CIA contractor, said the CIA wanted Whitlam removed from office because he threatened to close US military bases in Australia, including Pine Gap
Pine Gap is a satellite surveillance base and Australian Earth station approximately south-west of the town of Alice Springs, Northern Territory in the center of Australia. It is jointly operated by Australia and the United States, and since ...
. Boyce said Kerr was described by the CIA as "our man Kerr".
Whitlam later wrote that Kerr did not need any encouragement from the CIA. However, he also said that in 1977 United States Deputy Secretary of State
The deputy secretary of state of the United States is the principal deputy to the United States Secretary of State, secretary of state. The current deputy secretary of state is Wendy Ruth Sherman, serving since April 2021 under United States Secre ...
Warren Christopher
Warren Minor Christopher (October 27, 1925March 18, 2011) was an American lawyer, diplomat and politician. During Bill Clinton's first term as president, he served as the 63rd United States Secretary of State.
Born in Scranton, North Dakota, ...
made a special trip to Sydney to meet with him and told him, on behalf of US President Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he previously served as th ...
, of his willingness to work with whatever government Australians elected, and that the US would never again interfere with Australia's democratic processes.
Former ASIO
''Asio'' is a genus of typical owls, or true owls, in the family Strigidae. This group has representatives over most of the planet, and the short-eared owl is one of the most widespread of all bird species, breeding in Europe, Asia, North and S ...
chief Sir Edward Woodward has dismissed the notion of CIA involvement, as has journalist Paul Kelly. Justice Robert Hope, who had twice been royal commissioner investigating the Australian intelligence agencies, including ASIO, stated in 1998 that he had attempted to locate and interview a witness who had allegedly given in-camera evidence to the Church Committee
The Church Committee (formally the United States Senate Select Committee to Study Governmental Operations with Respect to Intelligence Activities) was a US Senate select committee in 1975 that investigated abuses by the Central Intelligence ...
about CIA involvement in the dismissal. He was unable to find either the witness or testimony, despite having the support of "a senior Ssenator". In his top secret supplementary report, however, Hope dismissed the idea of a CIA involvement in Australian politics.
Return to Opposition, 1975–1978
 As the ALP began the 1975 campaign, it seemed that its supporters would maintain their rage. Early rallies drew huge crowds, with attendees handing Whitlam money to pay election expenses. The crowds greatly exceeded those in any of Whitlam's earlier campaigns; in The Domain, Sydney, 30,000 people gathered for an ALP rally below a banner: "Shame Fraser Shame". Fraser's appearances drew protests, and a letter bomb sent to Kerr was defused by authorities. Instead of making a policy speech to keynote his campaign, Whitlam made a speech attacking his opponents and calling 11 November "a day which will live in infamy".
Polls from the first week of campaigning showed a nine-point swing against Labor, which would have decimated Labor if repeated in an election. Whitlam's campaign team disbelieved the results at first, but additional polling returns clearly showed that the electorate had turned against Labor. The Coalition attacked Labor for economic conditions, and released television commercials with the title "The Three Dark Years" showing images from Whitlam government scandals. The ALP campaign concentrated on the issue of Whitlam's dismissal and did not address the economy until its final days. By that time Fraser was confident of victory and content to sit back, avoid specifics and make no mistakes. In the election, the Coalition won the largest majority government in Australian history, winning 91 seats to Labor's 36. Labor suffered a 6.5 per cent swing against it and its caucus was cut almost in half, suffering a 30-seat swing. Labor was left with five fewer seats than it had when Whitlam took the leadership. The Coalition also won a 37–25 majority in the Senate.
Whitlam stayed on as Opposition leader, surviving a leadership challenge. In early 1976, an additional controversy broke when it was reported that Whitlam had been involved in ALP attempts to raise $500,000 during the election from the
As the ALP began the 1975 campaign, it seemed that its supporters would maintain their rage. Early rallies drew huge crowds, with attendees handing Whitlam money to pay election expenses. The crowds greatly exceeded those in any of Whitlam's earlier campaigns; in The Domain, Sydney, 30,000 people gathered for an ALP rally below a banner: "Shame Fraser Shame". Fraser's appearances drew protests, and a letter bomb sent to Kerr was defused by authorities. Instead of making a policy speech to keynote his campaign, Whitlam made a speech attacking his opponents and calling 11 November "a day which will live in infamy".
Polls from the first week of campaigning showed a nine-point swing against Labor, which would have decimated Labor if repeated in an election. Whitlam's campaign team disbelieved the results at first, but additional polling returns clearly showed that the electorate had turned against Labor. The Coalition attacked Labor for economic conditions, and released television commercials with the title "The Three Dark Years" showing images from Whitlam government scandals. The ALP campaign concentrated on the issue of Whitlam's dismissal and did not address the economy until its final days. By that time Fraser was confident of victory and content to sit back, avoid specifics and make no mistakes. In the election, the Coalition won the largest majority government in Australian history, winning 91 seats to Labor's 36. Labor suffered a 6.5 per cent swing against it and its caucus was cut almost in half, suffering a 30-seat swing. Labor was left with five fewer seats than it had when Whitlam took the leadership. The Coalition also won a 37–25 majority in the Senate.
Whitlam stayed on as Opposition leader, surviving a leadership challenge. In early 1976, an additional controversy broke when it was reported that Whitlam had been involved in ALP attempts to raise $500,000 during the election from the Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr
Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr ' (1 July 1914 – 4 October 1982) was the fourth president of Iraq, from 17 July 1968 to 16 July 1979. He was a leading member of the revolutionary Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party and later the Baghdad-based Ba'ath Party and ...
government of Iraq. No money had actually been paid, and no charges were filed.
The Whitlams were visiting China at the time of the Tangshan earthquake
The 1976 Tangshan earthquake () was a 7.6 earthquake that hit the region around Tangshan, Hebei, China, at 3:42 a.m. on 28 July 1976. The maximum intensity of the earthquake was XI (''Extreme'') on the Mercalli scale. In minutes, 85 percen ...
in July 1976, though they were staying in Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popul ...
, away from the epicentre. ''The Age
''The Age'' is a daily newspaper in Melbourne, Australia, that has been published since 1854. Owned and published by Nine Entertainment, ''The Age'' primarily serves Victoria (Australia), Victoria, but copies also sell in Tasmania, the Austral ...
'' printed a cartoon by Peter Nicholson showing the Whitlams huddled together in bed with Margaret Whitlam saying, "Did the earth move for you too, dear?" This cartoon prompted a page full of outraged letters from Labor partisans and a telegram from Gough Whitlam, safe in Tokyo, requesting the original of the cartoon.
In early 1977 Whitlam faced a leadership challenge from Bill Hayden
William George Hayden (born 23 January 1933) is an Australian politician who served as the 21st governor-general of Australia from 1989 to 1996. He was Leader of the Labor Party and Leader of the Opposition from 1977 to 1983, and served as ...
, the last treasurer in the Whitlam government, and won by a two-vote margin. Fraser called an election for 10 December. Although Labor managed to pick up five seats, the Coalition still enjoyed a majority of 48. According to Freudenberg, "The meaning and the message were unmistakable. It was the Australian people's rejection of Edward Gough Whitlam." Whitlam's son Tony
Tony may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Tony (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Gregory Tony (born 1978), American law enforcement officer
* Motu Tony (born 1981), New Zealand international rugby leagu ...
, who had joined his father in the House of Representatives at the 1975 election, was defeated. Shortly after the election, Whitlam resigned as party leader and was succeeded by Hayden.
Later years and death, 1978–2014
Whitlam was made aCompanion of the Order of Australia
The Order of Australia is an honour that recognises Australian citizens and other persons for outstanding achievement and service. It was established on 14 February 1975 by Elizabeth II, Queen of Australia, on the advice of the Australian Gove ...
in June 1978, and resigned from Parliament on 31 July of the same year. He then held various academic positions. When Labor returned to power under Bob Hawke
Robert James Lee Hawke (9 December 1929 – 16 May 2019) was an Australian politician and union organiser who served as the 23rd prime minister of Australia from 1983 to 1991, holding office as the leader of the Australian Labor Party (A ...
in 1983, Whitlam was appointed as Australia's ambassador to UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
, based in Paris. He served for three years in this post, defending UNESCO against allegations of corruption. At the end of his term as ambassador Whitlam was elected to the Executive Board of UNESCO for a 3-year term, until 1989. In 1985, he was appointed to Australia's Constitutional Commission
Many entities have been called a Constitutional Commission with the general purpose of reviewing a constitution, or planning to create one.
Afghanistan
* Afghan Constitution Commission
** Timeline of the War in Afghanistan (August 2003)
* Reigns ...
.
Whitlam was appointed chairman of the National Gallery of Australia
The National Gallery of Australia (NGA), formerly the Australian National Gallery, is the national art museum of Australia as well as one of the largest art museums in Australia, holding more than 166,000 works of art. Located in Canberra in th ...
in 1987 after his son Nick, who was then managing director of the State Bank of New South Wales, turned down the position. He and Margaret Whitlam were part of the bid team that in 1993 persuaded the International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
to give Sydney the right to host the 2000 Summer Olympics
The 2000 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXVII Olympiad and also known as Sydney 2000 (Dharug: ''Gadigal 2000''), the Millennium Olympic Games or the Games of the New Millennium, was an international multi-sport event held from 1 ...
.
Sir John Kerr died in 1991. He and Whitlam never reconciled; indeed, Whitlam always saw his dismissal from office as a "constitutional coup d'état". Whitlam and Fraser put aside their differences and became friends during the 1980s, though they never discussed the events of 1975. The two subsequently campaigned together in support of the 1999 Australian republic referendum
The Australian republic referendum held on 6 November 1999 was a two-question referendum to amend the Constitution of Australia. The first question asked whether Australia should become a republic with a President appointed by Parliament foll ...
. In March 2010, Fraser visited Whitlam at his Sydney office while on a book tour to promote his memoirs. Whitlam accepted an autographed copy of the book and presented Fraser with a copy of his 1979 book about the dismissal, ''The Truth of the Matter''.
During the 1990s Labor Government, Whitlam used the Australian Greens
The Australian Greens, commonly known as The Greens, are a confederation of Green state and territory political parties in Australia. As of the 2022 federal election, the Greens are the third largest political party in Australia by vote and th ...
as a "decoy questioner" in parliament. According to Dee Margetts
Diane Elizabeth Margetts (born 5 March 1955), known as Dee Margetts, is a former Australian politician. She was a member of the Australian Senate from 1993 to 1999 and a member of the Western Australian Legislative Council from 2001 to 2005, re ...
, Whitlam "didn't like what Keating and Hawke had done" and regularly sent the Greens questions to ask the government about policies he disagreed with.
 Whitlam initially had a close relationship with Labor leader
Whitlam initially had a close relationship with Labor leader Mark Latham
Mark William Latham (born 28 February 1961) is an Australian politician and media commentator, currently serving as a member in the New South Wales Legislative Council. He previously served as the leader of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) and ...
; however, by 2005 he had called for Latham's resignation from parliament. Whitlam called his support of Latham to enter federal politics as one of his "lingering regrets".
Whitlam supported fixed four-year terms for both houses of Parliament. In 2006, he accused the ALP of failing to press for this change. In April 2007, he and Margaret Whitlam were both made life members of the Australian Labor Party. This was the first time anyone had been made a life member of the party organisation at the national level.
In 2007, Whitlam testified at an inquest into the death of Brian Peters, one of five Australia-based TV personnel killed in East Timor in October 1975. Whitlam indicated he had warned Peters' colleague, Greg Shackleton, who was also killed, that the Australian government could not protect them in East Timor and that they should not go there. He also said Shackleton was "culpable" if he had not passed on Whitlam's warning.
Whitlam joined three other former prime ministers in February 2008 in returning to Parliament to witness the Federal Government apology to the Aboriginal Stolen Generations
The Stolen Generations (also known as Stolen Children) were the children of Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander descent who were removed from their families by the Australian federal and state government agencies and church miss ...
by the then prime minister Kevin Rudd
Kevin Michael Rudd (born 21 September 1957) is an Australian former politician and diplomat who served as the 26th prime minister of Australia from 2007 to 2010 and again from June 2013 to September 2013, holding office as the leader of the ...
. On 21 January 2009, Whitlam achieved a greater age () than any other prime minister of Australia, surpassing the previous record holder Frank Forde
Francis Michael Forde (18 July 189028 January 1983) was an Australian politician who served as prime minister of Australia from 6 to 13 July 1945. He was the deputy leader of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) from 1932 to 1946. He served as pri ...
. On the 60th anniversary of his marriage to Margaret Whitlam, he called it "very satisfactory" and claimed a record for "matrimonial endurance". In 2010, it was reported that Whitlam had moved into an aged care facility in Sydney's inner east in 2007. Despite this, he continued to go to his office three days a week. Margaret Whitlam remained in the couple's nearby apartment. In early 2012, she suffered a fall there, leading to her death in hospital at the age of 92 on 17 March of that year, a month short of the Whitlams' 70th wedding anniversary.
Gough Whitlam died on the morning of 21 October 2014. His family announced that there would be a private cremation and a public memorial service. Whitlam was survived by his four children, five grandchildren and nine great-grandchildren. He was the longest-lived Australian Prime Minister, dying at the age of 98 years and 102 days. He predeceased his successor Malcolm Fraser (14 years his junior) by just under five months. His funeral was attended by seven Australian prime ministers.
Memorials
Sydney Town Hall
The Sydney Town Hall is a late 19th-century heritage-listed town hall building in the city of Sydney, the capital city of New South Wales, Australia, housing the chambers of the Lord Mayor of Sydney, council offices, and venues for meetings an ...
and was led by Kerry O'Brien. The Welcome to Country
A Welcome to Country is a ritual or formal ceremony performed as a land acknowledgement at many events held in Australia. It is intended to highlight the cultural significance of the surrounding area to the descendants of a particular Aborigina ...
was given by Auntie Millie Ingram and eulogies were delivered by Graham Freudenberg, Cate Blanchett
Catherine Elise Blanchett (; born 14 May 1969) is an Australian actor. Regarded as one of the finest performers of her generation, she is known for her versatile work across independent films, blockbusters, and the stage. She has received nu ...
, Noel Pearson
Noel or Noël may refer to:
Christmas
* , French for Christmas
* Noel is another name for a Christmas carol
Places
* Noel, Missouri, United States, a city
* Noel, Nova Scotia, Canada, a community
* 1563 Noël, an asteroid
*Mount Noel, Briti ...
, John Faulkner
John Philip Faulkner (born 12 April 1954) is an Australian former Labor Party politician who was a Senator for New South Wales from 1989 to 2015. He was a Cabinet Minister in the Keating, Rudd and Gillard Governments.
After his election to ...
and Antony Whitlam. Pearson's contribution in particular was hailed as "one of the best political speeches of our time". Musical performances were delivered by William Barton (a didgeridoo
The didgeridoo (; also spelt didjeridu, among other variants) is a wind instrument, played with vibrating lips to produce a continuous drone while using a special breathing technique called circular breathing. The didgeridoo was developed by ...
improvisation), Paul Kelly and Kev Carmody
Kevin Daniel Carmody (born 1946), better known by his stage name Kev Carmody, is an Aboriginal Australian singer-songwriter and musician, a Murri man from northern Queensland. He is best known for the song "From Little Things Big Things Grow", ...
(their land rights protest song ''From Little Things Big Things Grow
"From Little Things Big Things Grow" is a protest song recorded by Australian artists Paul Kelly & The Messengers on their 1991 album ''Comedy'', and by Kev Carmody (with Kelly) on his 1993 album ''Bloodlines''. It was released as a CD singl ...
''), as well as the Sydney Philharmonia Choir and the Sydney Symphony Orchestra
The Sydney Symphony Orchestra (SSO) is an Australian symphony orchestra that was initially formed in 1908. Since its opening in 1973, the Sydney Opera House has been its home concert hall. Simone Young is the orchestra's chief conductor and firs ...
, conducted by Benjamin Northey
Benjamin Northey is an Australian conductor, musician and arranger. He has been Chief Conductor of the Christchurch Symphony Orchestra in New Zealand, since 2015.Bach's ''
 Whitlam remains well remembered for the circumstances of his dismissal. It is a legacy he did little to efface; he wrote a 1979 book, ''The Truth of the Matter'' (the title is a play on that of Kerr's 1978 memoir, ''Matters for Judgment''), and devoted part of his subsequent book, ''Abiding Interests'', to the circumstances of his removal. According to journalist and author Paul Kelly, who penned two books on the crisis, Whitlam "achieved a paradoxical triumph: the shadow of the dismissal has obscured the sins of his government".
More books have been written about Whitlam, including his own writings, than about any other Australian prime minister. According to Whitlam biographer Jenny Hocking, for a period of at least a decade, the Whitlam era was viewed almost entirely in negative terms, but that has changed. Still, she feels Australians take for granted programmes and policies initiated by the Whitlam government, such as recognition of China, legal aid, and Medicare.
Whitlam remains well remembered for the circumstances of his dismissal. It is a legacy he did little to efface; he wrote a 1979 book, ''The Truth of the Matter'' (the title is a play on that of Kerr's 1978 memoir, ''Matters for Judgment''), and devoted part of his subsequent book, ''Abiding Interests'', to the circumstances of his removal. According to journalist and author Paul Kelly, who penned two books on the crisis, Whitlam "achieved a paradoxical triumph: the shadow of the dismissal has obscured the sins of his government".
More books have been written about Whitlam, including his own writings, than about any other Australian prime minister. According to Whitlam biographer Jenny Hocking, for a period of at least a decade, the Whitlam era was viewed almost entirely in negative terms, but that has changed. Still, she feels Australians take for granted programmes and policies initiated by the Whitlam government, such as recognition of China, legal aid, and Medicare.
Gough Whitlam
ustralia's Prime Ministers / National Archives of Australia
The Whitlam Institute
The Whitlam Dismissal11 November 1975
opy of dismissal letter
Gurindji Land Ceremony Speech
ranscript and audio from August 1975 * Listen to an excerpt of Gough Whitlam'
'Kerr's Cur' speech
from the
"It's Time" speech
ranscript {{DEFAULTSORT:Whitlam, Gough 1916 births 2014 deaths 1975 Australian constitutional crisis Attorneys-General of Australia Australian barristers Australian Labor Party members of the Parliament of Australia Australian Leaders of the Opposition Australian ministers for Foreign Affairs Australian King's Counsel Australian republicans Australian agnostics Australian former Christians Australian social democrats Companions of the Order of Australia Honorary Grand Companions of the Order of Logohu Members of the Australian House of Representatives for Werriwa Members of the Australian House of Representatives Members of the Cabinet of Australia People educated at Canberra Grammar School People educated at Knox Grammar School People of the Vietnam War Permanent Delegates of Australia to UNESCO Politicians from Melbourne Prime Ministers of Australia Recipients of the Centenary Medal Recipients of the Order of the Rising Sun Royal Australian Air Force officers Royal Australian Air Force personnel of World War II Treasurers of Australia University of Sydney alumni Leaders of the Australian Labor Party Government ministers of Australia People from Kew, Victoria People from Canberra 20th-century Australian politicians 20th-century Australian lawyers
St Matthew Passion
The ''St Matthew Passion'' (german: Matthäus-Passion, links=-no), BWV 244, is a '' Passion'', a sacred oratorio written by Johann Sebastian Bach in 1727 for solo voices, double choir and double orchestra, with libretto by Picander. It sets ...
'', "Va, pensiero
"" (), also known as the "Chorus of the Hebrew Slaves", is a chorus from the opera ''Nabucco'' (1842) by Giuseppe Verdi. It recollects the period of Babylonian captivity after the loss of the First Temple in Jerusalem in 586 BCE.
The libretto i ...
" from Verdi's ''Nabucco
''Nabucco'' (, short for Nabucodonosor ; en, " Nebuchadnezzar") is an Italian-language opera in four acts composed in 1841 by Giuseppe Verdi to an Italian libretto by Temistocle Solera. The libretto is based on the biblical books of 2 Kings, ...
'', "Un Bal" from ''Symphonie fantastique
' (''Fantastical Symphony: Episode in the Life of an Artist … in Five Sections'') Op. 14, is a program symphony written by the French composer Hector Berlioz in 1830. It is an important piece of the early Romantic period. The first performan ...
'' by Berlioz and, as the final piece, ''Jerusalem'' by Parry
PARRY was an early example of a chatbot, implemented in 1972 by psychiatrist Kenneth Colby.
History
PARRY was written in 1972 by psychiatrist Kenneth Colby, then at Stanford University. While ELIZA was a tongue-in-cheek simulation of a Rogeria ...
. ''Jerusalem'' was followed by a flypast
A flypast is a ceremonial or honorific flight by an aircraft or group of aircraft. The term flypast is used in the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth. In the United States, the terms flyover and flyby are used.
Flypasts are often tied in w ...
of four RAAF
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
F/A-18 Hornets in missing man formation
The missing man formation is an aerial salute performed as part of a flypast of aircraft at a funeral or memorial event, typically in memory of a fallen pilot, a well-known military service member or veteran, or a well-known political figure. T ...
. Those attending the memorial included the current and some former governors-general, the current and all living former prime ministers, and members of the family of Vincent Lingiari
Vincent Lingiari (13 June 1908 or 1919 – 21 January 1988) was an Australian Aboriginal rights activist and member of the Gurindji people. In his early life he started as a stockman at Wave Hill Station, where the Aboriginal workers were g ...
. The two-hour service, attended by 1,000 invited guests and 900 others, was screened to thousands outside the Hall, as well as in Cabramatta
Cabramatta ('Cabra') is a suburb in south-western Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Cabramatta is located south-west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Fairfield.
Cabramat ...
and Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a met ...
, and broadcast live by ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
television.
In honour of Whitlam, the Australian Electoral Commission
The Australian Electoral Commission (AEC) is the independent federal agency in charge of organising, conducting and supervising federal Australian elections, by-elections and referendums.
Responsibilities
The AEC's main responsibility is to ...
created the Division of Whitlam
The Division of Whitlam is an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales.
Whitlam is an industrial and working-class electorate. It includes the cities of Wollongong and Shellharbor. Whitlam covers 1,331 square kilometers i ...
in the House of Representatives in place of the Division of Throsby
The Division of Throsby was an Australian electoral division in the state of New South Wales. The division was named after Charles Throsby, a prominent pioneer and explorer in the early nineteenth century of the areas to the south of Sydney. ...
, with effect from the 2016 election. ACT Chief Minister Katy Gallagher
Katherine Ruth Gallagher (born 18 March 1970) is an Australian politician who has been serving as the Minister for Finance, Minister for Women, Minister for the Public Service and Vice-President of the Executive Council in the Albanese Gover ...
announced that a future Canberra suburb will be named for Whitlam, and that his family would be consulted about other potential memorials. Gough Whitlam Park in Earlwood, New South Wales
Earlwood is a suburb in Southern Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Earlwood is located 10 kilometres south-west of the Sydney central business district, and is part of the St George area. It is in the local government areas ...
, is named after him.
In January 2021, the Whitlams' purpose-built home from 1956 to 1978 at 32 Albert Street, Cabramatta, designed by architect Roy Higson Dell Appleton, came up for sale. It was eventually sold at for $1.15 million to a group of Labor supporters, including former NSW Premier Barrie Unsworth
Barrie John Unsworth (born 16 April 1934) is a former Australian politician, representing the Labor Party in the Parliament of New South Wales from 1978 to 1991. He served as the 36th Premier from July 1986 to March 1988.
Early years
Unswort ...
, with the intention of restoring the house for educational purposes as a museum. The work is supported by a Commonwealth government national heritage grant of $1.3 million, and is to be managed by the Whitlam Institute
The Western Sydney University Parramatta Campus is one of ten Western Sydney University campuses. It is situated in the suburb of Parramatta in the City of Parramatta. The campus consists of two sites; Parramatta South Campus (main campus, at ...
of Western Sydney University
Western Sydney University, formerly the University of Western Sydney, is an Australian multi-campus university in the Greater Western region of Sydney, Australia. The university in its current form was founded in 1989 as a federated network ...
. The house was proposed to be listed as a local heritage item in the ''Fairfield Local Environmental Plan 2013'' as part of a regular LEP review, which identified the house as being at least of state heritage significance. Following renovations and restoration works, the "Whitlam Prime Ministerial Home" was officially opened by Prime Minister Anthony Albanese
Anthony Norman Albanese ( or ; born 2 March 1963) is an Australian politician serving as the 31st and current prime minister of Australia since 2022. He has been leader of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) since 2019 and the member of parlia ...
on 2 December 2022.
Legacy and historical evaluation
 Whitlam remains well remembered for the circumstances of his dismissal. It is a legacy he did little to efface; he wrote a 1979 book, ''The Truth of the Matter'' (the title is a play on that of Kerr's 1978 memoir, ''Matters for Judgment''), and devoted part of his subsequent book, ''Abiding Interests'', to the circumstances of his removal. According to journalist and author Paul Kelly, who penned two books on the crisis, Whitlam "achieved a paradoxical triumph: the shadow of the dismissal has obscured the sins of his government".
More books have been written about Whitlam, including his own writings, than about any other Australian prime minister. According to Whitlam biographer Jenny Hocking, for a period of at least a decade, the Whitlam era was viewed almost entirely in negative terms, but that has changed. Still, she feels Australians take for granted programmes and policies initiated by the Whitlam government, such as recognition of China, legal aid, and Medicare.
Whitlam remains well remembered for the circumstances of his dismissal. It is a legacy he did little to efface; he wrote a 1979 book, ''The Truth of the Matter'' (the title is a play on that of Kerr's 1978 memoir, ''Matters for Judgment''), and devoted part of his subsequent book, ''Abiding Interests'', to the circumstances of his removal. According to journalist and author Paul Kelly, who penned two books on the crisis, Whitlam "achieved a paradoxical triumph: the shadow of the dismissal has obscured the sins of his government".
More books have been written about Whitlam, including his own writings, than about any other Australian prime minister. According to Whitlam biographer Jenny Hocking, for a period of at least a decade, the Whitlam era was viewed almost entirely in negative terms, but that has changed. Still, she feels Australians take for granted programmes and policies initiated by the Whitlam government, such as recognition of China, legal aid, and Medicare. Ross McMullin
Ross McMullin (born 1952) is an Australian historian who has written a number of books on political and social history, as well as several biographies.
McMullin was educated at the University of Melbourne, where he wrote his Master of Arts thes ...
, who wrote an official history of the ALP, notes that Whitlam remains greatly admired by many Labor supporters because of his efforts to reform Australian government, and his inspiring leadership. Some rankings have put Whitlam high on the list of Australia's better prime ministers. Economist and writer Ross Gittins
Ross Gittins AM FRSN (born 1948 in Newcastle, Australia) is an Australian political and economic journalist and author, known for "his ability to make dry, hard-to-understand economics and economic policy relevant".
Early life and education
R ...
evaluates opinions on the Whitlam Government's responses to the economic challenges of the time:
Wallace Brown describes Whitlam in his book about his experiences covering Australian prime ministers as a journalist:
Whitlam's last words in the documentary film ''Gough WhitlamIn His Own Words'' (2002) were in response to a question about his status as an icon and elder statesman. He said:
Published works
* ''On Australia's Constitution'' (Melbourne: Widescope, 1977). * ''The Truth of the Matter'' (Melbourne: Melbourne University Press, 1979). * ''The Whitlam Government'' (Ringwood: Viking, 1985). * ''Abiding Interests'' (Brisbane: University of Queensland Press, 1997). * ''My Italian Notebook: The Story of an Enduring Love Affair'' (Sydney: Allen & Unwin, 2002)See also
* '' The Hon E.G. Whitlam'', painting byClifton Pugh
Clifton Ernest Pugh AO, (17 December 1924 – 14 October 1990) was an Australian artist and three-time winner of Australia's Archibald Prize. One of Australia's most renowned and successful painters, Pugh was strongly influenced by German Expr ...
* Whitlam Government
* First Whitlam Ministry
* Second Whitlam Ministry
* Third Whitlam Ministry
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Gough Whitlam
ustralia's Prime Ministers / National Archives of Australia
The Whitlam Institute
The Whitlam Dismissal11 November 1975
opy of dismissal letter
Gurindji Land Ceremony Speech
ranscript and audio from August 1975 * Listen to an excerpt of Gough Whitlam'
'Kerr's Cur' speech
from the
National Film and Sound Archive
The National Film and Sound Archive of Australia (NFSA), known as ScreenSound Australia from 1999 to 2004, is Australia's audiovisual archive, responsible for developing, preserving, maintaining, promoting and providing access to a national co ...
"It's Time" speech
ranscript {{DEFAULTSORT:Whitlam, Gough 1916 births 2014 deaths 1975 Australian constitutional crisis Attorneys-General of Australia Australian barristers Australian Labor Party members of the Parliament of Australia Australian Leaders of the Opposition Australian ministers for Foreign Affairs Australian King's Counsel Australian republicans Australian agnostics Australian former Christians Australian social democrats Companions of the Order of Australia Honorary Grand Companions of the Order of Logohu Members of the Australian House of Representatives for Werriwa Members of the Australian House of Representatives Members of the Cabinet of Australia People educated at Canberra Grammar School People educated at Knox Grammar School People of the Vietnam War Permanent Delegates of Australia to UNESCO Politicians from Melbourne Prime Ministers of Australia Recipients of the Centenary Medal Recipients of the Order of the Rising Sun Royal Australian Air Force officers Royal Australian Air Force personnel of World War II Treasurers of Australia University of Sydney alumni Leaders of the Australian Labor Party Government ministers of Australia People from Kew, Victoria People from Canberra 20th-century Australian politicians 20th-century Australian lawyers